Introduction
In today’s interconnected global economy, supply chains have become increasingly complex networks spanning continents, involving countless partners, and generating massive amounts of data. As businesses strive for efficiency and resilience, one approach stands out as transformative: Master Data Management (MDM).
The movement of goods and services from the point of origin to the final customer is a complicated process that is part of supply chain management. Master Data is a crucial element that is frequently overlooked in this complex web of operations.
The cornerstone of seamless, effective, and efficient supply chain operations is supply chain master data. It stands for important data that is utilized uniformly throughout the supply chain’s systems and operations. Supply chain master data will be discussed in this article along with its types, significance, and practical applications.
Let’s explore how MDM is revolutionizing supply chain operations and why it might be the competitive edge that any business needs.
Supply Chain Master Data
Supply Chain Master Data refers to the core, consistent data that is crucial for the effective functioning of a supply chain. It includes standardized information about products, suppliers, customers, locations, and other critical elements that support day-to-day business operations.
Master data is not transactional; rather, it represents entities that are used repeatedly across different systems or processes. This data typically doesn’t change frequently, but when it does, it has a significant impact on operations.
Before diving into MDM, let’s understand what we’re optimizing. A supply chain encompasses the entire journey of products or services from conception to delivery:
- Procurement: Sourcing raw materials and components from suppliers
- Manufacturing: Transforming these inputs into finished goods
- Storage: Managing inventory across warehouses and distribution centers
- Delivery: Getting products to customers efficiently and on time
Supply Chain Management (SCM) coordinates these activities to maximize efficiency and customer satisfaction. It involves strategic planning, building reliable supplier networks, accurately forecasting demand, and orchestrating complex logistics operations.
You can schedule a slot using the form below, and we’ll guide you through our products and their features. Additionally, you can receive a free POC using your own sample data.
Key Characteristics of Supply Chain Master Data
- Operational data: Day-to-day details like inventory and production schedules
- Transactional data: Records of orders, shipments, and payments
- Performance data: Metrics tracking supplier reliability and quality
- Predictive data: Forward-looking analytics to anticipate changes
But here’s the challenge: Without proper management, this data exists in silos, creating inconsistencies that lead to inefficiencies, missed opportunities, and increased vulnerability to disruptions.
The Data Challenge in Supply Chains
In a modern supply chain, every stage of the process—procurement, manufacturing, storage, transportation, and delivery—produces vast amounts of data. This data is crucial for making informed decisions, optimizing operations, and improving overall efficiency.
However, if not properly managed, supply chain data often exists in silos, meaning it is isolated within different departments, systems, or even companies. This fragmentation creates inconsistencies, inefficiencies, and missed opportunities, making businesses more vulnerable to disruptions.
Let’s break this down step by step to understand the different types of supply chain data and why managing it effectively is critical.
Inventory Levels Constantly Fluctuate
Businesses need to keep track of how much inventory is available at different locations (warehouses, distribution centers, retail stores, etc.).
Inventory levels change due to incoming shipments, sales, returns, and damage/loss.
If inventory data is inaccurate or delayed, businesses risk stockouts (losing sales due to insufficient stock) or overstocking (leading to unnecessary storage costs and potential waste).
Example: A retail chain might face issues if its central database shows a product is in stock at a store, but the actual inventory count is lower due to a recent spike in demand.
Shipping Schedules Vary in Real-Time
Shipments can be delayed due to weather, traffic, port congestion, customs clearance issues, or mechanical failures.
Businesses must track shipments in real time to anticipate delays and adjust logistics plans accordingly.
Example: A manufacturer relying on just-in-time inventory might need to halt production if a critical component is delayed, leading to production bottlenecks and increased costs.
Supplier Performance Varies Across Metrics
Every supplier has different levels of reliability, quality, lead times, and pricing.
Poor supplier performance can result in production delays, increased costs, and lower product quality.
Businesses need accurate supplier performance data to evaluate risks and make informed sourcing decisions.
Example: A company using multiple suppliers for raw materials needs to compare their on-time delivery rate, defect rate, and responsiveness to choose the most reliable partners.
Customer Demand Shifts with Market Trends
Demand is affected by seasonality, consumer behavior, economic conditions, and competitor actions.
Without accurate demand forecasting, companies may either overproduce (leading to wasted inventory and markdowns) or underproduce (resulting in lost sales).
This data falls into four key categories:
Operational Data
This includes real-time information on inventory, warehouse management, production schedules, and logistics.
It helps businesses monitor their daily operations and make tactical decisions.
Like a manufacturing company uses operational data to track machine performance and production output to prevent downtime.
Transactional Data
This data is recorded every time a financial or logistical transaction occurs in the supply chain, like purchase orders, invoices, shipping documents, payments, and customer returns.
Performance Data
This data includes KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) that measure supplier reliability, transportation efficiency, order accuracy, and warehouse productivity.
Businesses use this data to evaluate supplier contracts, optimize logistics, and improve service levels.
Like a logistics company tracks on-time delivery rates for its fleet to identify and address inefficiencies in its routing system.
Predictive Data
Predictive analytics uses historical data, AI, and machine learning models to anticipate future supply chain trends and risks.
Helps businesses adjust production schedules, optimize inventory levels, and proactively address potential bottlenecks.
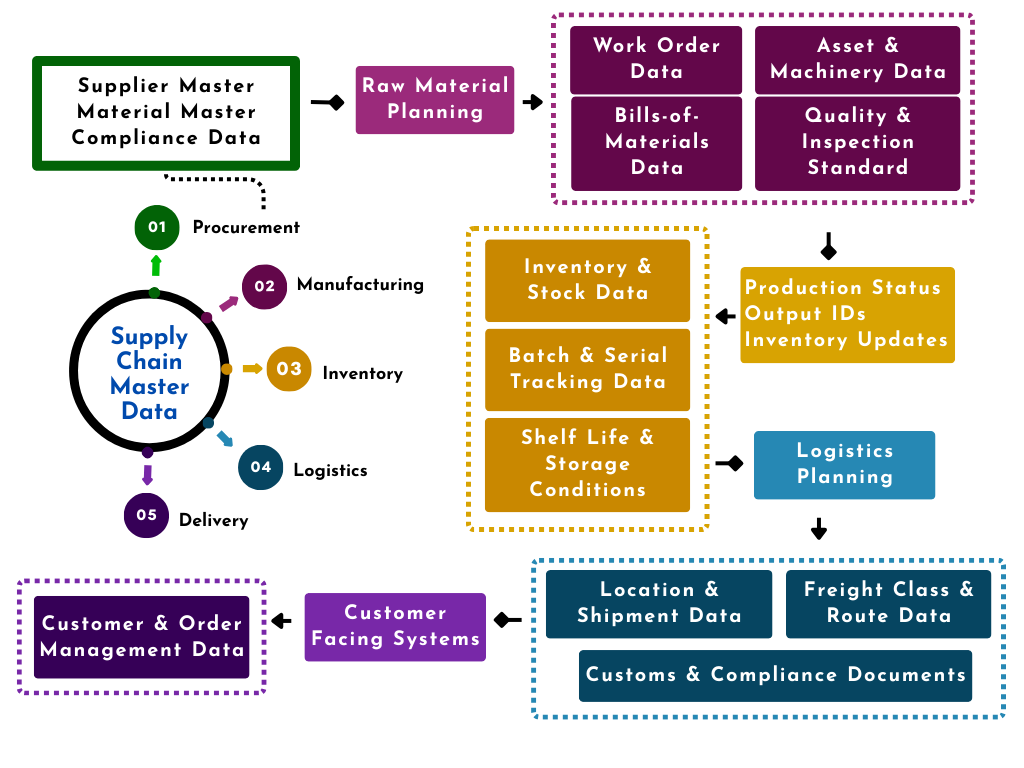
Types of Supply Chain Master Data
Supply chain master data can be divided into several categories, each supporting different aspects of the supply chain. Below are the key types of supply chain master data:
Product Master Data
Unlike traditional SCM approaches that often leave data management fragmented, MDM creates a single source of truth accessible across the organization. This fundamental difference transforms operations in multiple ways.
Product master data includes detailed information about the goods being produced, stored, or shipped through the supply chain. This data may include:
Product ID: A unique identifier for each product.
Description: A clear description of the product.
Specifications: Details like size, weight, color, material, and packaging.
Pricing: Standard cost, selling price, or contract pricing.
Lifecycle information: Product development stages, shelf-life, and obsolescence dates.
An oil refinery tracks valves, pipes, and pressure regulators essential for plant safety. A shutoff valve’s master data includes valve ID like VAL-300X, pressure rating like up to 2000 PSI, material type, and maintenance cycles, helping prevent equipment failures that could disrupt operations.
Supplier Master Data
Supplier master data contains all the information related to the suppliers that provide raw materials, components, or finished goods. It helps procurement teams manage relationships and track performance.
Key Components:
Supplier ID: Unique identifier for each supplier.
Supplier Name: The name of the supplier organization.
Contact Information: Addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses.
Payment Terms: Agreed payment conditions, such as credit terms and early payment discounts.
Compliance and Certification Information: Details about the supplier’s certifications, audit history, and compliance to regulatory standards.
A copper mining company sources spare parts for excavators and conveyor belts from multiple vendors. Supplier master data includes supplier ID (SUP-EXC-092) lead times, quality certifications (ISO 14001, MSHA compliance), and contract terms, enabling better procurement decisions and minimizing equipment downtime.
Customer Master Data
Customer master data contains the necessary information about the businesses or individuals that purchase the products or services from a company. This data allows sales teams to understand their customer base and make strategic decisions.
Key Components:
Customer ID: A unique identifier for each customer.
Customer Name: Name of the organization or individual.
Billing and Shipping Addresses: Information about where invoices should be sent and where products need to be delivered.
Order History: A record of past orders and transactions with the customer.
Credit Limit: The maximum amount of credit extended to the customer.
A machinery manufacturer supplies equipment to construction and mining firms. By tracking purchase records, service contracts, and credit terms, ensures timely equipment servicing and enhances customer loyalty.
Location Master Data
Location master data includes information about the physical locations involved in the supply chain. This includes warehouses, distribution centers, stores, and customer delivery points.
Key Components:
Location ID: A unique identifier for each location.
Location Name: Name or description of the location (e.g., “Chicago Warehouse”).
Geographical Details: Address, region, and proximity to key transportation routes.
Capacity Information: Information about storage or processing capacity.
A global beverage company maintains master data for bottling plants (PLANT-ATL-001), warehouses, and distribution centers. Accurate location details help optimize supply routes, reduce transit costs, and improve delivery timelines.
Inventory Master Data
Inventory master data focuses on the details related to the physical goods in storage and across the supply chain network.
Key Components:
Inventory ID: Unique identifier for each inventory item.
Stock Level: The quantity of products available at a particular time.
Warehouse Location: Information on where each product is stored.
Replenishment Lead Time: The time it takes to replenish stock.
An oil drilling company stocks drill bits like DRILLBIT-T600, mud pumps, and blowout preventers across offshore rigs. Inventory data, including location-based stock levels and expected consumption rates, ensures vital components are available when needed, avoiding costly downtime.
How MDM Enhances Supply Chain Resilience
In an era of unprecedented supply chain disruptions, resilience has become a top priority. MDM strengthens this resilience through:
Enhanced Visibility and Risk Mitigation
With centralized data, organizations gain comprehensive visibility into their supply networks. This panoramic view enables proactive risk management and strategic supplier diversification before problems arise.
Real-Time Decision-Making
When disruptions occur, integrated tracking systems provide immediate insights, allowing teams to respond with agility. Meanwhile, predictive analytics powered by clean, consistent data help organizations develop robust contingency plans.
Improved Supplier Collaboration
Unified supplier data streamlines communication and coordination. This enhanced collaboration optimizes order timing and significantly reduces costly stockouts.
Data Driven Crisis Response
During major disruptions, MDM proves invaluable by quickly identifying alternative suppliers and logistics options, enabling rapid pivoting to maintain business continuity.
Strengthened Compliance and Sustainability
As regulatory requirements grow increasingly complex, MDM helps track compliance metrics across the supply chain. Additionally, it supports sustainability initiatives by monitoring environmental impacts and promoting eco-friendly practices.
Cost and Efficiency Gains
By eliminating data silos and redundancies, MDM drives substantial cost savings while improving inventory management through accurate, consistent information.
Innovation and Long-Term Agility
Perhaps most importantly, MDM creates the foundation for technological innovation, supporting advanced capabilities like digital twins for process optimization and sophisticated trend analysis.
The Tangible Impact of MDM on Supply Chain Functions
The benefits of MDM aren’t theoretical – they transform specific supply chain functions in measurable ways:
Inventory Management
- Dramatic reduction in stock discrepancies through accurate and consistent product identification
- Improved forecasting accuracy with reliable historical data
- Optimized safety stock levels based on precise lead times
- Reduced obsolescence through better product lifecycle tracking
While optimizing MRO inventory data, a manufacturing plant producing hydraulic pumps and motors uses MDM to synchronize Bill of Materials (BOM) data across ERP and warehouse management systems. By ensuring consistent part numbers, specifications, and storage locations, MDM prevents duplicate inventory entries, reducing discrepancies and improving production planning.
Procurement and Supplier Management
- Consolidated supplier views enabling strategic sourcing decisions
- Standardized contractual terms across business units
- Enhanced supplier performance monitoring
- Streamlined onboarding of new suppliers
- Enhanced visibility of commercial aspects like pending payments, payment milestones etc.
Within a procurement data management, a refinery procures valves, gaskets, and heat exchangers from multiple global suppliers. MDM consolidates supplier qualification data, lead times, and compliance certificates into a centralized procurement dashboard, ensuring that procurement teams always select approved vendors with validated part compatibility and safety certifications.
Logistics and Distribution
- Optimized transportation planning with accurate location data
- Improved route efficiency through consistent delivery information
- Enhanced visibility across complex transportation networks
- Reduced shipping errors and returns
- Real-time updates on material dispatch, delivery and receipt
A factory producing turbines and generators ships components to multiple global sites. MDM integrates with transportation management systems (TMS) to maintain accurate route data, freight class codes, and customs clearance documents, preventing shipping delays and reducing import/export compliance risks.
Demand Planning and Forecasting
- More accurate demand signals through consistent product identification
- Improved statistical forecasting with clean data
- Better customer and product segmentation for targeted planning
- Enhanced pattern identification across markets
A mining company extracts and processes bauxite for aluminum production. MDM consolidates geological survey data, historical extraction rates, and global aluminum demand trends, allowing predictive models to recommend optimal extraction schedules and refinery throughput rates.
Order Management and Fulfillment
- Reduced order errors through consistent information
- Improved perfect order rates and customer satisfaction
- Enhanced delivery timeline accuracy
- Streamlined order-to-cash processes
A contract manufacturer assembling printed circuit boards (PCBs) receives bulk orders from multiple clients. MDM standardizes customer order specifications, approved component lists, and assembly line configurations, reducing production errors and ensuring that orders match engineering tolerances and compliance standards.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
- Common language and data definitions across departments
- Improved decision-making with consistent information
- Enhanced ability to scale operations with standardized processes
- Better alignment between supply chain and other business functions
A mining site operates haul trucks, crushers, and conveyor belts. MDM integrates IoT-based equipment health monitoring with procurement systems, ensuring that wear part replacements are ordered proactively based on usage data, reducing unplanned downtime.
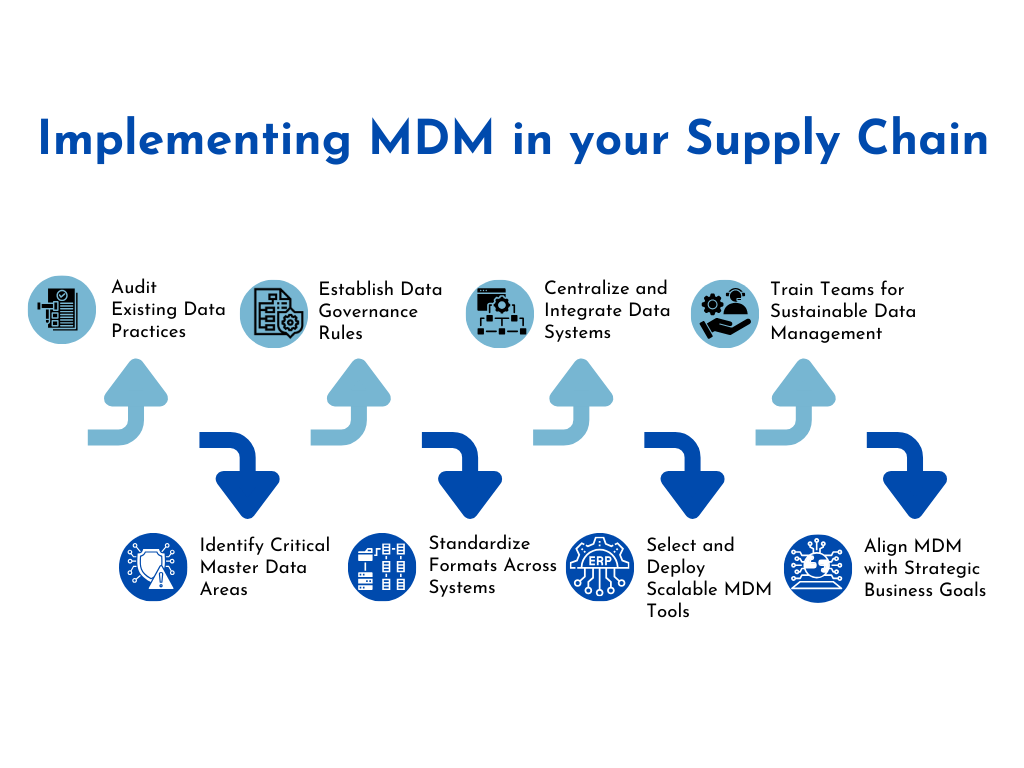
Implementing MDM in Your Supply Chain
Assess Current Practices – Identify inefficiencies in supplier data, inventory records, and logistics tracking. Address issues like duplicate entries, inconsistent formats, and missing details.
Define Key Master Data Domains – Focus on product, supplier, customer, location, and inventory data to streamline procurement, production, and distribution.
Develop Governance Frameworks – Establish data ownership, approval workflows, and validation rules to maintain accuracy, compliance, and consistency.
Standardize Data Formats – Ensure uniform naming conventions, measurement units, and data fields across ERP, WMS, and procurement systems.
Bridge Data Gaps – Validate missing or outdated information using internal cross-references and external sources like supplier databases and regulatory records.
Consolidate Disparate Data – Migrate legacy systems into a centralized MDM platform, enabling real-time data synchronization and eliminating silos.
Select Scalable MDM Solutions – Choose software with integration capabilities, automation features, and AI-driven insights for predictive supply chain management.
Train Your Team – Conduct role-specific training for procurement, logistics, and IT teams to ensure proper usage and governance of MDM tools.
Monitor and Maintain Data Quality – Implement automated audits and periodic manual reviews to detect errors, redundancies, and outdated records.
Align MDM with Business Goals – Integrate MDM with analytics, sustainability tracking, and market expansion plans to drive efficiency and competitiveness.
Conclusion
In today’s volatile business environment, supply chain excellence is no longer optional – it’s essential not only for growth but also for survival. Master Data Management transforms supply chains from potential vulnerability points into strategic assets, enabling organizations to operate with greater efficiency, agility, and resilience.
By creating a single source of truth for critical data, MDM empowers businesses to make better decisions, respond more effectively to disruptions, and ultimately deliver superior value to customers. The actual question isn’t “Whether you can afford to implement MDM in your supply chain” – it’s “Whether you can afford not to”.
As global supply chains continue to face unprecedented challenges, those with robust MDM capabilities will be best positioned to weather storms, seize opportunities, and thrive in the future of commerce.





