Introduction to Service Data Management
A fast-paced and ever-evolving business landscape demands accurate and well-structured master data. Service master data management and cleansing play a pivotal role in ensuring operational efficiency, compliance, and informed decision-making across industries. Poorly managed or inaccurate service data can lead to procurement inefficiencies, regulatory risks, and operational delays, while clean and structured data enables cost savings, improved supplier relationships, and strategic agility.
This blog explores the details of service master data management, its relevance in the industrial landscape, and the critical importance of maintaining clean and accurate service data. We will also explore how businesses can unlock competitive advantages by investing in robust service data management practices.
Before diving into the details of service master data management, let us first examine the key differences between material master data management and service master data management.
Companies focus on using Master Data Management solutions to cover materials, customers, and supplier data. One segment that is often overlooked is the services master. Despite being a high spend area, services master data management is still a fairly new concept to many, and companies are reluctant to invest.
Yet, similar to material master data, services masters have grown both in size and complexity over the decades and without streamlined processes, are often unstructured, inconsistent, and difficult to manage. Companies face multiple challenges and incur avoidable costs due to bad, inconsistent and unreliable services data. Some of these challenges are:
- Lack of data standards and data entry protocols
- Extensive duplication
- Poor visibility across locations
- Rogue spending
- Inability to reduce procurement costs
Services Master Data Management cleans, streamlines, and automates the service master for consistent, accurate data with organization wide visibility. With a clean, consolidated, and de-duplicated single source of truth, it is easier to analyze data, cut unnecessary costs, and make informed decisions. An SMDM solution won’t just cleanse data temporarily but will provide a sustainable, repeatable solution by defining data cleansing rules, structuring data according to category, group, and numbers, building consistent service descriptions and providing on-going data governance to maintain the quality of services master.
Key Differences Between Material Master and Service Master Data Management
In the world of master data management, Material Master and Service Master Data are two distinct yet essential components that organizations rely on for streamlined operations. While both play a critical role in procurement, inventory management, and operational efficiency, their purposes, structure, and usage differ significantly. Below are the key distinctions:
Definition and Scope
Material Master Data
Represents physical items such as raw materials, components, finished goods, or spare parts. It includes information like material type, unit of measure, stock quantity, and storage location, focusing on inventory management and supply chain processes.
Service Master Data
Refers to intangible offerings such as consultancy, maintenance, logistics, or IT services. It captures details like service descriptions, pricing structures, service categories, and provider information, emphasizing the management of non-physical resources.
Nature of Data
Material Master Data
Quantifiable and measurable, materials have defined attributes such as Size, Material, Weight and expiration dates. These attributes enable tracking and monitoring throughout the supply chain.
Service Master Data
Non-quantifiable and qualitative in nature, services are defined through descriptive details such as scope, duration, and service levels rather than physical attributes.
Usage in Business Processes
Material Master Data
Supports processes like inventory management, production planning, and procurement of goods. Materials are stored, tracked, and physically managed within warehouses or production facilities.
Service Master Data
Facilitates service procurement, contract management, and vendor performance evaluation. Services are typically delivered on-site, remotely, or through third-party providers and are not stored physically.
Classification Standards
Material Master Data
Often categorized using internal classification systems or external standards such as UNSPSC, E-class for uniformity in supply chain operations.
Service Master Data
Commonly classified using global standards like UNSPSC, which help in categorizing services for procurement and spend analysis.
Complexity of Management
Material Master Data
Often categorized using internal Relatively straightforward to manage due to its tangible and repeatable nature. Inventory systems and ERP platforms provide robust tools for material tracking and management.systems or external standards such as UNSPSC, E-class for uniformity in supply chain operations.
Service Master Data
More complex to manage due to the subjective and customized nature of services. It requires detailed descriptions, governance frameworks, and frequent updates to remain relevant.
While material master data is well-defined and supported by traditional ERP systems, Service Master Data Management is often overlooked despite being equally critical to business success, both Material Master and Service Master Data are integral to business operations, understanding their key differences is crucial for effective master data management. Material Master Data focuses on the physical flow of goods, while Service Master Data revolves around the efficient management of intangible services. In this blog, we will focus more on Service Master Data Management and explore the strategies, tools, and best practices that organizations can use to ensure the efficient handling, tracking, and optimization of service data across business functions.
Trusted By Industry Leaders Worldwide






What is Service Master Data Management and Why it is required?
Service master data refers to the foundational information related to services that a company procures, provides, or manages. This includes service descriptions, pricing, categorizations, vendor or service provider details, and relevant industry-specific classifications such as UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code) and E-class. For example, a service like “IT Support” can be mapped to UNSPSC code “81111811-Technical support or help desk services”, ensuring its consistent identification across systems and vendors. Similarly, “Office Cleaning Services” may correspond to UNSPSC code “76111500-General building and office cleaning and maintenance services”, making procurement more streamlined and accurate.
When services are not properly classified or linked to standard codes, discrepancies arise. For instance, if “IT Support” is erroneously classified under a general category such as “Consulting Services,” it can lead to procurement inefficiencies and compliance risks. Moreover, this misclassification may result in financial misstatements, as costs might be allocated incorrectly, affecting budgets and forecasting accuracy.
Service master data management involves the systematic process of creating, maintaining, and governing this data to ensure it is accurate, consistent, and up-to-date, ultimately supporting better financial oversight and operational effectiveness.

A Comprehensive Guide to Service Master Data Management for Modern Enterprises
Effective Service Master Data Management (MDM) is essential for businesses to streamline operations, optimize costs, and ensure compliance with industry standards. A well-structured approach to service data management requires a focus on several key areas:
Standardized Classification: Services must be categorized using globally recognized standards like UNSPSC to ensure uniformity across business units and systems. Standardization eliminates inconsistencies caused by varying naming conventions and facilitates seamless integration with enterprise applications such as ERP and procurement platforms. This approach supports better spend analysis, enhances compliance with procurement regulations, and improves overall data transparency.
Accurate Data Entry: Precision at the data entry stage is critical to prevent cascading errors and inefficiencies downstream. Errors in service data lead to duplicate entries, flawed reporting, and poor decision-making. By enforcing validation rules and training employees in best practices, businesses can build a solid foundation for service data quality, minimizing operational costs and errors.
Governance Framework: A robust governance framework ensures accountability, defines ownership, and establishes workflows for service data management. It helps maintain data integrity by preventing unauthorized changes and aligns data management practices with organizational strategies. Governance frameworks are also vital for meeting compliance and audit requirements.
Technology Enablement: Leveraging advanced MDM software solutions is critical for centralizing, validating, and monitoring service data. Automation through these tools supports data classification, deduplication, and enrichment, significantly boosting efficiency and accuracy. Integration with AI/ML technologies further enhances insights by identifying patterns and anomalies, enabling businesses to remain agile and competitive in dynamic markets.
Regular Data Audits: Periodic audits ensure service data remains accurate, relevant, and aligned with current business needs. These reviews help identify and correct discrepancies, duplications, and outdated information. Audits also uncover opportunities for cost savings, such as consolidating redundant services or renegotiating contracts, while reducing risks of compliance failures.
Interdepartmental Collaboration: Effective service data management requires collaboration between procurement, finance, operations, and IT teams. Procurement teams bring insights into vendor-specific service details, finance focuses on cost allocation accuracy, and IT ensures seamless system integration. This cross-functional alignment ensures service data reflects the organization’s broader goals and fosters consistency across departments.
Scalability and Flexibility: Service MDM systems must be scalable to accommodate business growth and flexible to adapt to changing needs. As businesses expand, the variety and volume of services increase, necessitating systems capable of managing large datasets and complex service hierarchies. Flexibility ensures adaptability to new regulations, market trends, and technological advancements.
Key Challenges in Managing Service Data Effectively
Service data management is a cornerstone of operational efficiency, particularly in industries that rely heavily on outsourced services or complex procurement networks. However, managing service data effectively is fraught with unique challenges. Unlike material data, which deals with tangible items, service data is intangible, diverse, and often unstructured. These characteristics make it more difficult to classify, standardize, and manage effectively. Below, we explore the key challenges businesses face in managing service data and how these issues can impact operations.
Lack of Standardized Classification
One of the primary challenges in managing service data is the absence of consistent classification standards. Services, unlike materials, are often described differently by various stakeholders, leading to inconsistent entries in service master data.
Impact: This inconsistency hampers integration with enterprise systems like ERP and procurement platforms, complicating spends analysis and vendor comparisons.
Solution: Adopting globally recognized classification systems, such as UNSPSC, can help ensure uniformity and make data more accessible across departments.
Inconsistent and Incomplete Data
Service data often lacks the structured attributes found in material data, making it prone to errors and omissions. For example, incomplete service descriptions or missing pricing details can lead to inefficiencies in procurement and vendor management.
Impact: Incomplete data causes delays in service delivery, increases procurement costs, and creates challenges in decision-making.
Solution: Implementing data validation processes and mandatory data fields can help maintain data completeness and accuracy.
Difficulty in Quantifying Services
Unlike materials, which can be measured and tracked in units, services are qualitative in nature and often lack clear quantifiable metrics. This makes it challenging to assess the value and performance of services.
Impact: The inability to quantify services results in poor vendor performance tracking and difficulty in cost allocation.
Solution: Defining measurable service-level agreements (SLAs) and key performance indicators (KPIs) can help quantify and evaluate service quality.
Decentralized Data Management
Service data is often scattered across various departments, such as procurement, finance, and operations, with no centralized repository.
Impact: This decentralization leads to data duplication, discrepancies, and siloed information, which undermines collaboration and consistency.
Solution: Investing in a centralized master data management (MDM) system allows for better data governance and ensures that service data remains consistent and accessible across the organization.
High Complexity and Diversity of Services
Services vary significantly across industries and vendors, from one-time consultancy engagements to recurring maintenance contracts. This diversity adds complexity to service master data management.
Impact: Managing such varied data without proper categorization leads to inefficiencies in procurement and makes reporting more cumbersome.
Solution: Categorizing services into predefined hierarchies and leveraging advanced classification tools can simplify data management.

Lack of Ownership and Governance
Without clear accountability, service data management often falls through the cracks. Departments may create duplicate or inconsistent entries due to the lack of defined ownership and governance policies.
Impact: Poor governance results in data errors, audit failures, and reduced confidence in service data quality.
Solution: Establishing a governance framework that defines roles, responsibilities, and approval workflows ensures accountability and adherence to data quality standards.
Limited Use of Technology
Many organizations still rely on manual processes or outdated tools for managing service data, which are neither scalable nor efficient.
Impact: Limited technological adoption leads to slow data processing, human errors, and an inability to adapt to changing business needs.
Solution: Leveraging advanced MDM platforms equipped with AI and automation capabilities can enhance data accuracy, deduplication, and scalability.
Frequent Data Changes and Updates
Service data often requires frequent updates due to changing vendor agreements, pricing structures, or regulatory requirements.
Impact: Without proper version control and monitoring mechanisms, these changes can result in outdated or incorrect data being used in critical processes.
Solution: Regular data audits and automated update mechanisms help maintain up-to-date and accurate service data.
Key Steps in Service Data Management
Service data management is a crucial component of any organization’s data governance framework. With services playing a central role in modern business operations, effective service data management can lead to improved procurement practices, enhanced compliance, and operational efficiency. The following are the key steps in the service data management process, from data collection to validation.
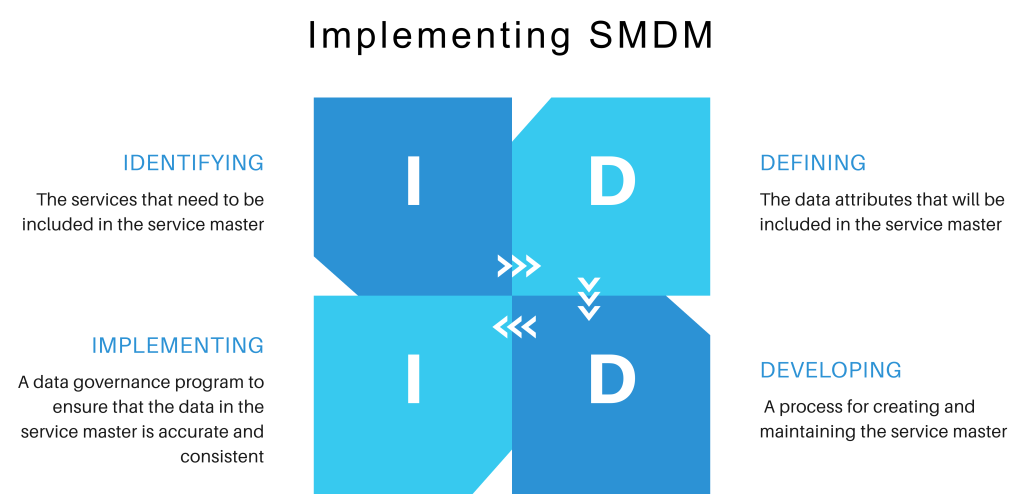
Data Collection: Sources of Service Data
The first step in effective service data management is the collection of service-related information. This involves gathering data from multiple internal and external sources to ensure a comprehensive and accurate record of all services provided or received by the organization.
Common sources of service data include:
Contracts: These contain detailed descriptions of services, pricing structures, service level agreements (SLAs), and terms and conditions. Contracts serve as a primary reference for data related to the scope, duration, and cost of services.
Invoices: Invoices provide critical data on service usage, pricing, discounts, payment terms, and dates of service delivery. They are vital for tracking the financial aspect of service procurement.
Procurement Systems: These systems contain records of service purchases, including vendor information, service specifications, quantities, and payment history. They are key sources for tracking ongoing or recurring services.
Service Requests and Work Orders: In organizations with maintenance or operations teams, work orders and service requests serve as sources of real-time service data, documenting requests for specific services and their status.
Collecting service data from multiple systems helps create a comprehensive and accurate picture of the services an organization uses, ensuring that the data reflects the latest transactions and agreements.
Classification: Grouping Services Using Appropriate Taxonomies
Once service data is collected, the next crucial step is classification—grouping services into categories that can be easily managed, compared, and analysed. Effective classification helps streamline procurement, improve spend analysis, and ensure that services are aligned with business objectives.
Common classification systems include:
UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code): This global classification standard categorizes services into segments, families, classes, and commodities, ensuring consistency across procurement systems and markets. For example, consulting services could be categorized under the segment “Professional Services,” with further subcategories for specific types of consulting (e.g., IT consulting).
E-class: This system is widely used in Europe and is particularly helpful for industries like manufacturing and engineering. It allows for more granular classification of services, with an emphasis on attributes that define the nature of the service.
We will explore UNSPSC and E-class topic in greater detail as we progress through this blog.
Custom Taxonomies: Some organizations may develop their own custom classification systems based on internal requirements or industry-specific needs.
Proper classification helps improve visibility and transparency into service-related spending and allows businesses to quickly assess service performance across categories.
Validation: Ensuring Service Descriptions, Units of Measure, and Prices Align with Business Requirements
After collecting and classifying the service data, the next step is validation—ensuring that the data aligns with business requirements and is accurate, complete, and up to date. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the data and minimizing errors or discrepancies that could impact decision-making.
Key validation activities include:
Service Descriptions: Ensuring that service descriptions are accurate, clear, and consistent with internal and vendor-specific documentation. The description should match the agreed scope of work and meet the organization’s quality standards.
Units of Measure (UOM): Verifying that the units of measure (e.g., hours, pieces, contracts) are consistent with business standards and are appropriate for the type of service being provided. For example, if a service is billed by hours, the UOM should clearly reflect this to avoid billing disputes.
Pricing and Terms: Ensuring that pricing information, payment terms, and discounts are consistent with contracts and agreements. Regularly validating service pricing is especially important in long-term contracts where price adjustments or service additions may occur.
Compliance Checks: Ensuring that services comply with industry regulations, internal policies, and quality standards. This is critical in sectors like healthcare, finance, and government, where non-compliance could lead to legal or financial consequences.
Validating service data is an ongoing process that helps ensure that services are being provided and paid for correctly, improving financial control and reducing the risk of errors and disputes.
Download Case Study

Elevating Operational Performance with Enhanced Data Quality in Electric Utilities
Leveraging Standards Like UNSPSC and E-class for Service Data
Effective service data management is critical for driving operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and cost optimization. However, the complexity and diversity of service data often make it difficult to organize, classify, and standardize. This is where globally recognized standards like UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code) and E-class play a pivotal role. These classification systems provide structured frameworks for categorizing service data, enabling consistency across systems, regions, and industries.
Overview of UNSPSC and E-class
UNSPSC
UNSPSC is a global classification system designed to categorize products and services uniformly. It uses a hierarchical structure of codes with multiple levels:
E-Class
E-class is another globally recognized classification system, primarily popular in Europe. It enables standardization of product and service data across industries and systems. E-class offers:
UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code)
UNSPSC is a global classification system designed to categorize products and services uniformly. It uses a hierarchical structure of codes with multiple levels:
Segment: Broad category (e.g., Services).
Family: Narrower category within the segment (e.g., Professional Services).
Class: More specific grouping within the family (e.g., Consulting Services).
Commodity: The most granular level (e.g., IT Consulting).
This hierarchical design allows businesses to drill down into detailed classifications while maintaining a high-level overview. UNSPSC is widely adopted in procurement, spend analysis, and e-commerce platforms.
E-class
E-class is another globally recognized classification system, primarily popular in Europe. It enables standardization of product and service data across industries and systems. E-class offers:
A detailed taxonomy with attributes for describing products and services.
Support for multiple languages and compliance with international standards.
Flexibility for mapping to other standards like UNSPSC.
UNSPSC and E-class are widely used in manufacturing, engineering, and procurement to standardize both product and service data.
How UNSPSC and E-class Help in Categorizing and Standardizing Service Data
Improved Data Consistency and Accuracy
Adopting a standardized classification system like UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code) or E-class ensures uniform data entry across all departments, business units, and systems. Without standardized coding, different teams may use varying terminologies, leading to inconsistencies in service descriptions and procurement records. These inconsistencies can result in incorrect data interpretation, erroneous spend reports, and inefficiencies in supplier communication. By implementing a structured framework, businesses eliminate duplication, reduce manual errors, and improve overall data quality, which in turn enhances decision-making and reporting.
Enhanced Spend Analysis and Procurement Efficiency
Standardized service data plays a crucial role in procurement strategies by enabling precise spend analysis. Organizations can categorize services under specific UNSPSC or E-class codes, facilitating the identification of cost-saving opportunities and spend trends.
Cost Benchmarking: Categorizing IT services, consulting, or facility management under standard codes allows companies to compare costs with industry benchmarks, identifying overpriced services.
Supplier Rationalization: With clear categorization, businesses can analyse their supplier base, consolidate procurement, and negotiate better contracts, leading to bulk discounts and improved supplier performance.
Fraud Detection: Proper categorization aids in identifying anomalies such as duplicate invoices, overbilling, or unnecessary expenditures, which might otherwise go unnoticed in an unstructured dataset.
Seamless Integration Across Systems
Enterprise-wide systems such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), procurement platforms, and analytics tools require a common language for data exchange. Standardized service classification enables smooth integration between these systems, ensuring seamless data flow across procurement, finance, and operations. Benefits include:
Automated Workflows: Correct categorization enables automation in procurement approvals, budgeting, and expense tracking, reducing manual intervention.
Interoperability: Standardized codes support cross-border transactions by aligning procurement data with international suppliers, minimizing discrepancies in service descriptions.
Enhanced Reporting: Organizations can generate accurate reports by aggregating services under common categories, improving visibility into procurement trends and cost allocation.
Compliance with Global Standards
Adhering to classification systems like UNSPSC and E-class ensures compliance with international procurement regulations and reporting standards. This minimizes the risks associated with regulatory non-compliance, such as penalties, contract disputes, and legal ramifications. Key compliance benefits include:
Transparency in Audits: Regulatory bodies and auditors can easily track and verify procurement transactions when services are categorized correctly.
Alignment with Tax and Legal Regulations: Many jurisdictions require specific service classifications for taxation and compliance purposes, ensuring accurate tax reporting and reducing financial risks.
Avoidance of Trade Restrictions: Proper classification helps businesses adhere to trade agreements and avoid procurement-related trade restrictions or sanctions.
Scalability and Flexibility
Both UNSPSC and E-class are designed to support business growth and adaptability. As companies expand their service offerings, they can seamlessly integrate new categories without disrupting existing procurement processes. Additionally, these classification systems allow businesses to:
Adapt to Market Changes: Service categories can be updated to reflect emerging technologies, industry shifts, and evolving business needs.
Support Multi-Region Operations: Global companies can standardize service procurement across multiple regions, ensuring consistency in data entry and reporting.
Improve Strategic Decision-Making: With a well-structured classification system, procurement teams can easily analyse service costs, supplier performance, and contract efficiencies.
SERVICE MASTER DATA- CLASSIFICATION
Risks of Incorrect Classification
Failure to accurately classify services can lead to significant operational and financial challenges, including:
Incorrect Budget Allocation: Misclassified services may be assigned to incorrect cost centers, leading to budget overruns or mismanagement.
Inaccurate Spend Analysis: If services are improperly categorized, procurement teams may fail to identify cost-saving opportunities, resulting in inefficient spending.
Regulatory Non-Compliance: Misclassification can lead to incorrect tax reporting, causing legal penalties and financial losses.
Supplier and Contract Mismanagement: Businesses might negotiate contracts based on inaccurate service classifications, leading to unfavourable terms or unnecessary expenditures.
Operational Disruptions: Wrong classification in automated procurement systems may result in delayed service fulfilment, incorrect invoicing, or compliance failures.
Potential Disasters from Poor Classification
Incorrect classification of services can lead to major business disruptions and financial losses. Some of the worst-case scenarios include:
Fraud and Financial Losses: Without proper classification, businesses may pay for duplicate or non-existent services, leading to fraud and revenue leakage.
Contractual and Legal Disputes: Misclassification can result in contracts being misaligned with service expectations, leading to disputes, litigation, or contract terminations.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Incorrectly categorized services may cause procurement teams to engage with the wrong suppliers, leading to delays, service failures, or compromised quality.
Reputational Damage: Regulatory violations, inefficiencies, and poor supplier management stemming from misclassification can harm an organization’s reputation and stakeholder trust.
Implementing UNSPSC and E-class for service data classification enhances data accuracy, improves procurement efficiency, ensures compliance, and supports business scalability. However, organizations must invest in proper implementation, training, and periodic audits to prevent misclassification-related risks. A well-structured classification system enables businesses to make informed procurement decisions, optimize spending, and maintain operational excellence in an increasingly complex global marketplace.
Practical Examples: Mapping Services to UNSPSC Codes for Global Standardization
Automated, Software-based Approach
An IT consulting firm can use UNSPSC to standardize its service offerings:
Segment: 80000000 (Management and Business Professionals and Administrative Services)
Family: 80100000 (Management advisory services)
Class: 80101500 (Business and corporate management consultation services)
Commodity: 80101507 (Information technology consultation services)
This ensures that all IT consulting services are categorized consistently, enabling precise spend analysis, vendor comparison, and procurement efficiency.
Example 2: Water Leakage Maintenance Services
A corporate firm requiring maintenance services can map them using UNSPSC:
Segment: 70000000 (Building and Facility Construction and Maintenance Services)
Family: 72100000 (Building and facility maintenance and repair services)
Class: 72101500 (Building maintenance and repair services)
Commodity: 72101510 (Plumbing system maintenance or repair)
Standardizing maintenance services under UNSPSC ensures clarity in procurement contracts, efficient vendor management, and compliance with industry regulations.
Example 3: E-class for Engineering Services
Using E-class, an engineering company can define specific service attributes for detailed classification:
E-class code:
15220100 Centrifugal pump (maintenance)
15220101 Centrifugal pump (inspection)
15220102 Centrifugal pump (servicing)
15220103 Centrifugal pump (repair)
15220104 Centrifugal pump (improvement)
This categorization allows detailed reporting and integration with other standards, ensuring accuracy across platforms.
UNSPSC and E-class offer powerful frameworks for categorizing and standardizing service data, enabling businesses to overcome challenges like inconsistency, inefficiency, and lack of global alignment. By leveraging these standards, organizations can enhance data quality, optimize procurement processes, and unlock valuable insights through better analytics.
In a world where businesses are increasingly interconnected, adopting robust classification standards like UNSPSC and E-class is not just a best practice but a strategic necessity for achieving operational excellence and staying competitive in the global market.
Future Trends in Service Data Management
As businesses continue to evolve in a digital-first world, service data management is undergoing a transformation driven by emerging technologies and automation. The ability to manage, standardize, and validate service data efficiently is becoming increasingly critical for organizations looking to optimize procurement, improve compliance, and enhance decision-making. Below are two key trends shaping the future of service data management.
Adoption of AI for Service Data Standardization
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way organizations classify, validate, and manage service data. AI-driven automation helps businesses overcome common challenges such as inconsistent service descriptions, duplicate records, and manual classification errors.
Key Benefits of AI in Service Data Management:
Automated Classification: AI algorithms can map service descriptions to standard taxonomies like UNSPSC and E-class, ensuring consistency across systems.
Duplicate Detection & Data Cleansing: Machine learning models can identify redundant or conflicting service entries and suggest corrections, leading to higher data accuracy and reduced procurement inefficiencies.
Context-Aware Data Enrichment: AI can analyse historical service transactions and recommend additional metadata, such as pricing benchmarks or vendor ratings, to enhance decision-making.
For example, AI-powered tools can automatically classify a consulting service under UNSPSC Code 80101500 (Business and Corporate Management Consultation Services), reducing manual effort and improving procurement transparency.
Real-Time Data Updates and Validation in the Cloud
With businesses increasingly adopting cloud-based procurement and ERP systems, real-time service data management is becoming a necessity. Cloud platforms enable seamless data synchronization across multiple departments, ensuring consistent and up-to-date service records.
Key Advantages of Cloud-Based Service Data Management
Instant Data Updates: Changes to service descriptions, pricing, and contract details can be reflected across all systems in real time, reducing errors and misalignment.
Automated Data Validation: Cloud platforms can integrate with external data sources and AI-driven validation engines to check for inconsistencies, missing fields, or incorrect classifications.
Scalability & Flexibility: Cloud solutions can handle large volumes of service data without performance degradation, making them ideal for growing enterprises with expanding service portfolios.
For instance, a global company using a cloud-based MDM (Master Data Management) system can instantly update service rates across regional offices, ensuring compliance with contractual agreements and enhancing financial forecasting accuracy.
Let’s look at some benefits of implementing a Services Master:
A single centralized source of truth
An integrated SMDM solution ensures all cleansed and standardized master data is stored at a single location in the cloud, easily accessible from across locations. It further leads to improved cross-plant collaboration and real-time visibility into any updates to the master data.
Consistent, structured descriptions
An advanced services master ensures corporate wide consistent, structured, reliable descriptions and services linked to global classification standards like UNSPSC.
Process and performance improvement
With a centralized, cleansed services master, companies have access to data at their fingertips. This data doesn’t just help in analysing performance and making corporate decisions but also helps in eliminating duplicates and enables on-time maintenance routines. Automated workflows and process streamlining helps clear bottlenecks and delays and ensures smooth and seamless process flow and improved ERP performance.
Advanced search capabilities
With multiple search features like ‘free-text search’, ‘search by category’, etc., finding the necessary services data with the help of just a keyword, a category, or an attribute becomes easy and quick. This improves visibility, reduces unnecessary purchases, and gives a granular view of the entire services master data.
Improved data security
An SMDM can ensure a heightened level of data security with user authentication role-based data access to only authorized personnel. Access logs can provide an audit trail with time stamps and improve individual accountability. With insecure activities getting flagged automatically, any unauthorized breach of data is contained.
Digitization and industrial revolution 4.0 have reiterated the importance of good quality data and the repercussions of depending on sub-standard, unreliable data. With data influencing strategic decisions, improving processes and productivity, and reducing costs, a cleansed, standardized services master can come with a host of opportunities and benefits for an organization. Be an early adopter of services master data management and get an edge over your competition!
Conclusion
Service master data management is a critical component of modern business operations, enabling organizations to achieve data consistency, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. By implementing standardized classification systems (UNSPSC, E-class), leveraging AI-driven automation, and adopting cloud-based MDM solutions, businesses can significantly improve their procurement efficiency, optimize costs, and ensure strategic agility.
Failure to manage service master data effectively can lead to severe consequences, including procurement inefficiencies, financial misstatements, compliance risks, and missed cost-saving opportunities. Standardization and rigorous governance frameworks are essential for preventing these risks and ensuring data integrity.
How Verdantis Can Help
Verdantis, a leader in Master Data Management solutions, offers powerful tools like Harmonize and Integrity to help organizations manage and cleanse their service master data. These solutions provide:
Automated Data Harmonization: Ensuring consistency by standardizing service descriptions, classifications, and attributes.
Data Cleansing & Enrichment: Identifying duplicates, correcting errors, and enriching service data with missing attributes.
AI-Powered Classification: Leveraging AI to map services to global standards like UNSPSC and E-class automatically.
Seamless Integration: Enabling real-time data synchronization across ERP, procurement, and analytics platforms.
Governance & Compliance Support: Implementing workflows that maintain data integrity and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
By leveraging Verdantis’ cutting-edge technology, businesses can eliminate inefficiencies, optimize procurement processes, and enhance overall data quality, making service master data management a strategic asset rather than a challenge. Investing in the right tools and methodologies ensures that organizations remain competitive and well-equipped to navigate the complexities of modern procurement and service management.





