Data governance, especially in the context of Master Data Management has grown exponentially in terms of popularity in the recent times. As enterprises realized the value of clean data and the efficiencies it can drive across procurement, supply chain, maintenance and product teams, and the exorbitant costs of periodic data cleansing activities, the demand for robust data governance has skyrocketed. There are implementation strategies for master data governance that companies can adopt, while implementing SAP MDG.
Given that SAP is one the market leaders for ERP solutions, especially for asset-intensive enterprises, the company has rolled out it’s own data governance product to manage a multi-domain master data implementation
The solution, quite simply is named SAP MDG, short for Master Data Governance.
So the discipline of governing master data in SAP as well as the product itself is also referred to as SAP MDG.
Related Article: How to Manage SAP MDM
What is SAP MDG & What Does it Do?
As mentioned earlier, MDG is part of a broader Data Management suite of products that is paid for and licensed separately from the SAP store.
The product supports all master data types and has built-in use cases for Data Deduplication, compliance, approvals, replication & standardization.
MDG supports and can be deployed in SAP ECC, S4/hana and as a cloud-based solution as well.
Interested users can take a free trial/demo for certain MDG cloud versions via SAP’s business technology platform
The product’s pricing may vary based on whether the company or user would want to support materials, suppliers, customers, finance, or multiple domains
Book a session with our master data expert using the form below to explore effective master data governance implementation strategies. Additionally, get a free proof of concept using your own sample data!
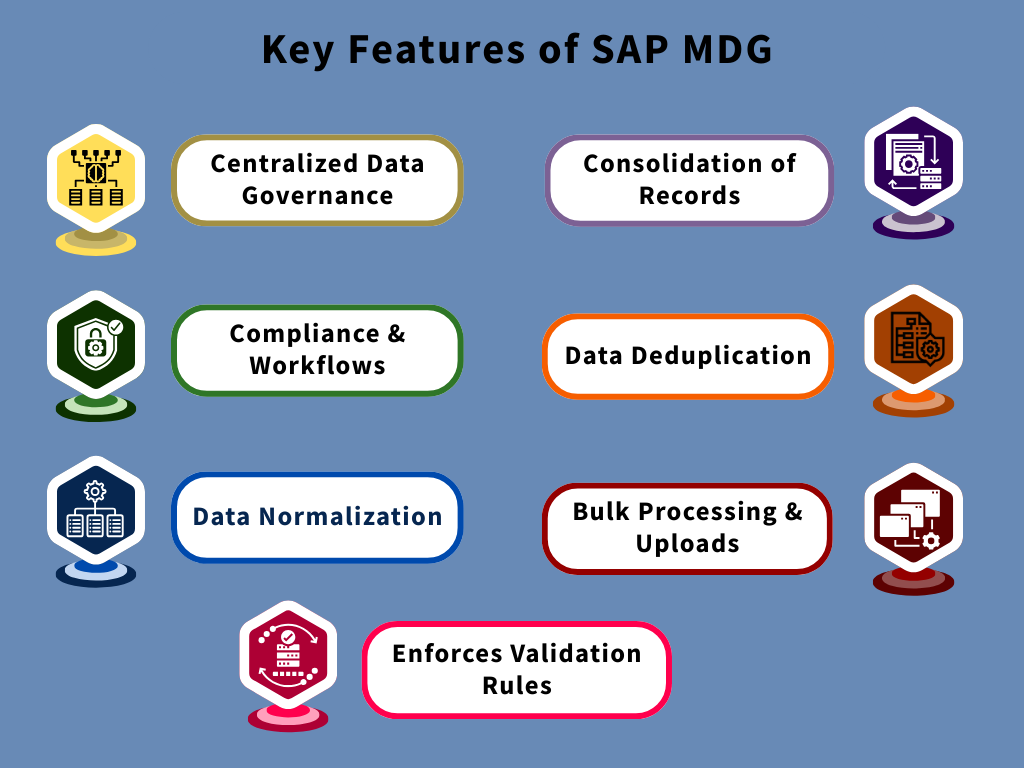
Centralized Data Governance
Easily one of the most important benefits of SAP MDG. Large enterprises have complex supply chains, distribution centres, manufacturing plants and facilities.
Many of them use use different instances of SAP or other ERPs altogether – like Oracle Cloud or MS Dynamics, all of which integrate with SAP MDG for one single unified view of org data.
This helps companies make strategic decisions across functions, spare parts can be extended to different plants; different suppliers for the same spart part or product can be consolidated with a stronger negotiating power and consumption patters of some customer cohorts can be analyzed at a global scale, regardless of which source system hosts the data.
Compliance & Workflows
Complex workflows and approval systems can be created within SAP MDG to establish better data stewardship standards. Workflows and sub-workflows are used to ensure accountability and visibility of data creation and updates in the system across the organizational hierarchy.
For example; in the case of supplier master, a steward from the procurement team may request the empanelment of a new supplier who supplies a maintenance spare part; a workflow can be set in a way such that the maintenance engineer requests a spare part, which then moves to the data steward for approval, after moving to approval stages to the Maintenance and Procurement heads.
MDG allows for creation of simple to advanced workflows and enforces compliances and approvals with tech-enabled processes.
Data Normalization
Data normalization is a critical piece in overall master data governance, SAP MDG uses rule-based normalization via business framework plus to systematically structure raw and messy data in descriptions and loose text
Through these rules, the software can process data in bulk as well as standardize and correct erroneous data at the time of entry – For instance, it can automatically convert values like “US”, USA to “United States of America”.
Through similar configurations, it can standardize units-of-measure, currency formats and other naming conventions based on on centralized framework and rule.
This structuring is essential to introduce any automations or business rules into any given process and is a hygiene requirement for any master data governance software worth its salt.
Moreover, MDG integrates directly with SAP data services to enable more advanced data cleansing and quality control tasks like parsing proper names, nouns, addresses , standardizing phone numbers and formatting etc.
Bulk Processing & Uploads
While this feature doesn’t exactly pertain to governance, it is quite a useful feature, through which, the same data records and values are processed retrospectively on legacy data.
These can be processed via CSV, XML or even through SAP data services that we mentioned earlier.
However, a critical shortcoming in this regard is – poor mechanisms to enrich data from external sources and lack of industry-specific training built into the software that increases manual workload for the data steward or ERP maintenance teams.
Data Deduplication
Like Verdantis’ data cleansing services for MRO parts, offered in Integrity; SAP MDG also de-duplicates data at two levels.
The first one being de-duplicating the records based on the standard available fields like description, record ID, MFR name or Part Number.
The second level of de-duplication is done by scoring potential duplicates by analyzing overlapping attributes along with units of measure and leveraging fuzzy logic for flagging likely duplicates for human review.
Consolidation of Records
MDG also merges data from different source systems, documents and files and applies its own match and merge logic for a relatively holistic and cleaner view of org data.
This can be done in batches or in as a continous integration of data records.
Enforces Validation Rules
The software also allows for configuration of validation rules for different types of Master Data. This can include configuration of “mandatory fields”, “minimum character length’ “maximum character length” “Alphanumeric or date formats” etc.
This ensures that no entry is ingested into the system without a certain level of sanity check and since this can be configured relatively flexibly in MDG, it makes data stewardship quite straightforward.
Executing Master Data Governance in SAP Systems
As good as SAP MDG is, especially considering that the product was released way back in 2011, it’s not free from some major drawbacks.
Moreover, there have been few updates in terms of features and performance, mostly around embedded AI but with questionable use-cases for practical applications
In more than 70% of the projects, our recommendation is generally to use SAP MDG along with a bolt-on solution for modern features that have been trained for industry-specific use-cases.
In the sections below, we will share data governance features from basic to advanced that any governance solution should solve for; and we will compare the solution(s) offered by SAP MDG (if any) and what could some alternatives be.
Limitations of MDG & Alternatives
The introduction of SAP MDG in 2011 was undoubtedly a welcome move and a step in the right direction for data management in ERP as a practice, however, as is the case with any product that has been around for this long, with little changes, its limitations have become glaringly obvious.
Technical Know-how
Managing large data sets spread across different silos was never expected to be simple and straightforward but the general critique of MDG has been the difficulty and complexity of the software beyond what is really necessary.
In most cases, an SAP data governance specialist needs to be hired internally who dedicatedly manages the workflows and operations of SAP MDG.
Many paid SAP MDG courses exist simply so that companies can hire the right talent for a very complex software that can be made much more simpler and straightforward.
Integrations with Non-SAP Systems
While the out-of-the-box integrations with SAP systems is quite intuitive and adaptive, integrations with non-sap systems are custom implementations and requires quite a bit of development bandwidth.
Since it’s fairly common for large organizations to use different ERPs across geographies and functions, this factor inevitably turns out to be an impediment.
Limited Coverage for All Master Data Domains
There are a few master data domains that SAP MDG manages quite well, mainly, Materials, Business Partner, Customers and Finance; for other domains like employees, equipments etc, the support is quite a bit on the lower side.
Moreover, some industries, especially in retail, energy production, healthcare and mining can require extensive customizations, making the entire governance initiative unsustainable.
Lacks Built-in Enrichment Methods
One of the biggest challenges with Master data management is limited or incomplete information
Several master data management software solutions solve for this by using AI-enabled processes or structured, proprietary databases that they maintain within their software solution.
Many of these software tools also leverage web-based extraction and fetch data from verified supplier websites, PDF documents etc, many of them can also detect obsolete supplier parts and suggest alternatives too.
In case of customer master, especially at B2B companies, integrations options with B2B contact and company intelligence softwares like ZoomInfo, DnB etc is very limited.
Limited AI Functionalities
There a few sectors and disciplines that can genuinely benefit and be fueled with Artificial Intelligence.
Data management is certainly one of them and the applications across data normalization, enrichment, governance and integrations are immense and we’re witnessing this first-hand at Verdantis.
In late 2024, SAP MDG announced the launch of an AI-assistant, which is certainly a welcome move but the practical applications for actual master data management remain unclear.
Integrity© for Master Data Governance
A lot of organizations provide SAP master data management solutions that are compatible with the ERP. Verdantis’ Integrity, which is also compatible with SAP MDG, is a holistic master data governance solution so enterprises across industries can manage and maintain ERP data seamlessly to avoid data quality issues and periodic data cleansing activities.
Integrity can either be used alongside MDG as a bolt-on solution or can be used independently in most popular ERPs like S4/Hana, ECC, Oracle JD Edwards, MS Dynamics.
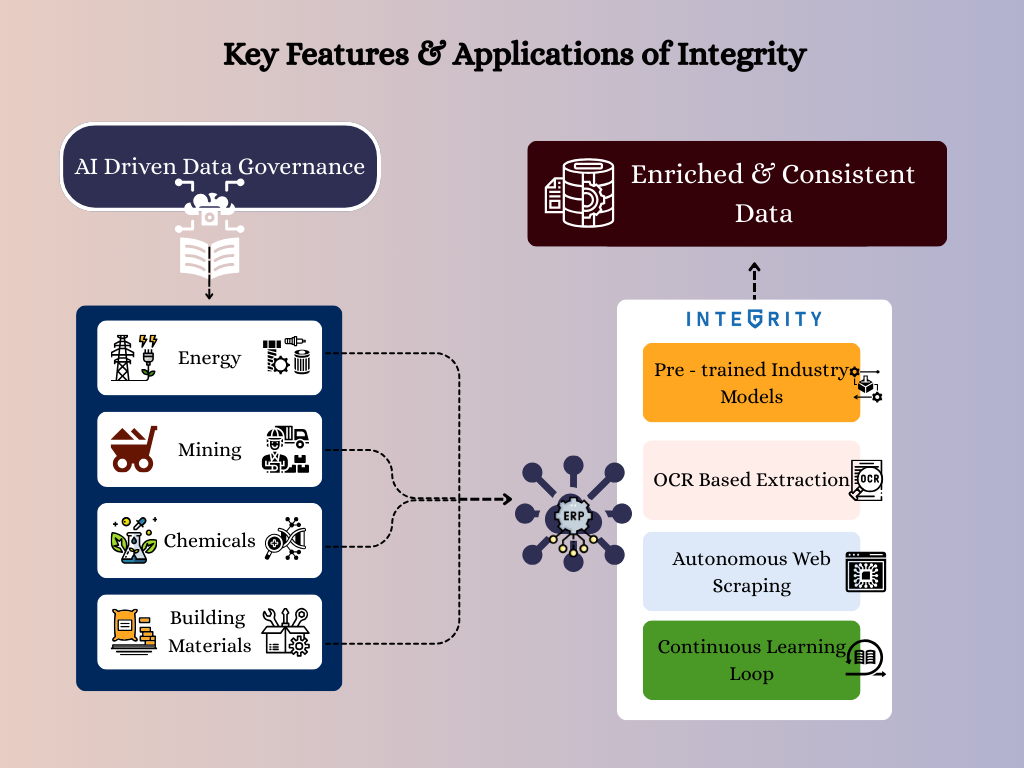
The software solution is purpose-built for companies in manufacturing or production-heavy operations; like Oil, Gas & Energy, Mining & Metals, Building Materials, Chemical Manufacturing and so on.
We detail some of the features, their applications and the key challenges that are Integrity solves for that simply isn’t possible in MDG OR is too complicated.
Industry-Specific Context
Integrity is specifically trained for data governance on MRO spare parts, materials, suppliers and equipment data that are used in asset intensive industries, especially across energy, mining, chemicals and building materials.
This trained information, along with an industry-adapted modifiers, rules and third-party data means that the processed data is far more accurate and “complete” before the data is even inputted into the ERP system.
You can also read our client use cases below to implement data governance practices to achieve a more structured, enriched and reliable data.
Governance with Embedded AI
Integrity is an AI-first data governance software, this means that the core-processes and functionalities are heavily driven by AI and machine learning.
When combined with powerful software workflows like autonomous web-scraping, OCR-based extraction and pre–trained industry models – it directly translates to very quick, accurate and reliable data processing
Continuous Learning
Since the software is an AI-first model, any erroneously processed data record can be re-trained with the corrected output during the human review stage.
The embedded Gen-AI models are programmed to learn from this user input and prevents similar erroneous outputs from cropping up again in the future
Seamless Integration
One of the key drawbacks of SAP MDG that we mentioned earlier had to do with limited integration options non-erp systems, this has been a leading problem at large enterprises since complex supply chains generally deploy multiple ERP systems and versions across for different requirements across functions and geographies.
Unlike MDG, process flows and operations in Integrity are fully no-code, even complex processing tasks and workflows are extremely user-intuitive and requires absolutely no technical bandwidth or programming experience.
Yes, a certain level of technical understanding pertaining to the data is required but this is already taken care of in most cases since the users have a solid understanding of the context in the underlying datapoints.
No-Code & User-Intuitive
Unlike MDG, process flows and operations in Integrity are fully no-code, even complex processing tasks and workflows are extremely user-intuitive and requires absolutely no technical bandwidth or programming experience.
Yes, a certain level of technical understanding pertaining to the data is required but this is already taken care of in most cases since the users have a solid understanding of the context in the underlying datapoints.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while SAP MDG offers strong master data governance capabilities, its complexity, limited integration options, and lack of built-in enrichment features can present significant challenges for organizations.
While there are other master data governance software solutions, Integrity by Verdantis stands out as a more advanced and intuitive solution, especially for asset-intensive industries like oil, gas, and mining. Powered by AI and machine learning, Integrity offers seamless integration, no-code workflows, and industry-specific data enrichment, making it a more efficient and user-friendly choice.
Its ability to streamline data governance with minimal technical expertise required sets it apart as a more adaptable and future-ready solution for modern enterprises.






