The oil and gas industry is undergoing a fundamental transformation in how it manages inventory and master data, driven by digital technologies, operational complexities, and the need for enhanced efficiency.
With global oil production at approximately 94.5 million barrels per day and the inventory management market valued at USD 3.21 billion in 2024, projected to reach USD 6.58 billion by 2033, effective inventory management has become critical for industry success.
This comprehensive analysis examines leading implementations across Middle Eastern and American companies, providing insights into best practices, technological solutions, and strategic outcomes.
What is Oil and Gas Inventory Management?
Oil and Gas Inventory Management refers to the systematic process of tracking, controlling, and optimizing the materials, spare parts, tools, and equipment used across the oil and gas value chain – including exploration, drilling, production, refining, and distribution.
In this industry, inventory isn’t limited to finished products like crude oil or refined fuels – it also includes Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) items, such as valves, pumps, compressors, gaskets, sensors, filters, and lubricants. These components are essential for maintaining production uptime and ensuring operational safety.
Because oil and gas operations are spread across remote sites, offshore platforms, pipelines, and refineries, managing inventory efficiently becomes a mission-critical task. A single missing spare part can halt production and cause costly downtime, while overstocking ties up millions in working capital.
Effective oil and gas inventory management involves:
-
Accurate Master Data: Clean, standardized, and enriched material records for precise tracking.
-
Demand Forecasting: Anticipating future material needs based on maintenance and production plans.
-
Spare Parts Optimization: Identifying critical components to prevent equipment failures.
-
Real-Time Visibility: Monitoring inventory levels across multiple sites and systems.
-
Governance and Automation: Ensuring data consistency and compliance with industry standards like ISO 14224 and API 6D.
When managed effectively, oil and gas inventory systems help companies reduce procurement costs, avoid unplanned downtime, improve maintenance efficiency, and ensure asset reliability.






Why Data Management Matters in Oil & Gas
The oil and gas value chain – from upstream exploration to downstream refining – operates in complex, distributed environments. Each segment faces unique inventory management pressures:
Upstream (Exploration & Drilling):
Managing spares for drilling rigs, wellheads, mud pumps, and blowout preventers, often across remote offshore or desert locations.Midstream (Transportation & Storage):
Maintaining compressors, pipeline valves, meters, and safety equipment across pumping stations and terminals.Downstream (Refining & Distribution):
Handling spare parts for reactors, turbines, exchangers, and control systems with precise material traceability.
Across these sectors, data inconsistencies lead to duplicate procurement, overstocking, unplanned downtime, and compliance risks.
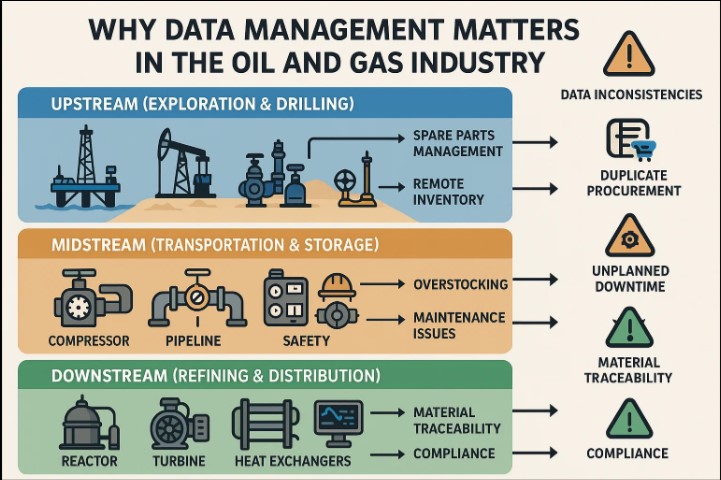
Core Components of Oil & Gas Inventory Management
|
Component |
Description |
Key Processes / Techniques |
Oil & Gas Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1. Inventory Planning & Optimization |
Determines what materials and spares to stock, where, and in what quantities to minimize costs and downtime. |
– ABC/XYZ classification- Min/Max levels- Safety stock- EOQ & reorder points |
A refinery plans additional gasket and seal kits before annual maintenance shutdowns based on historical usage. |
|
2. Demand Forecasting |
Predicts material requirements using consumption patterns and maintenance data to avoid overstocking or stockouts. |
– Historical usage trends- AI/ML-driven predictive models- Preventive maintenance integration |
Upstream operator forecasts mud pump seal replacements every 90 days, preventing rig downtime. |
|
3. Spare Parts & Criticality Management |
Categorizes spares by criticality to prioritize stocking of vital components. |
– Criticality analysis- Failure impact study- Maintenance prioritization |
Compressor bearings marked as “critical” due to potential production halt if unavailable. |
|
4. Procurement & Supplier Management |
Ensures timely and cost-effective sourcing of inventory from reliable suppliers. |
– Vendor rationalization- Long-term contracts- Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) |
Midstream operator implements VMI for pipeline valves to maintain just-in-time availability. |
|
5. Warehouse & Storage Management |
Organizes physical stock for efficient handling and traceability across sites. |
– Bin location system- RFID/barcode tagging- FIFO/FEFO- Layout optimization |
RFID-tagged equipment enables automated tracking of drilling spares and chemical drums. |
|
6. Real-Time Visibility & Analytics |
Provides a unified view of stock levels, consumption, and replenishment needs across multiple facilities. |
– ERP integration- IoT-enabled tracking- Predictive dashboards |
LNG terminal integrates maintenance and inventory data to auto-trigger reorders for pump spares. |
|
7. Obsolescence & Lifecycle Management |
Identifies and removes outdated or inactive parts to reduce inventory bloat. |
– Periodic audits- Lifecycle tracking- Disposal or resale of obsolete items |
Drilling company removes old sensor models after system upgrades to digital instrumentation. |
|
8. Inventory Valuation & Cost Control |
Tracks financial impact and efficiency of inventory operations. |
– FIFO/LIFO valuation- Carrying cost analysis- Inventory turnover ratio |
Refinery cuts holding costs by 20% after eliminating duplicate and inactive spare parts. |
|
9. Compliance, Safety & Environmental Management |
Ensures safe handling and legal compliance for hazardous materials and inventory. |
– HAZMAT classification- MSDS tracking- ISO/OSHA compliance audits |
Offshore rig maintains digital MSDS for chemicals to meet safety and environmental norms. |
|
10. Digital Transformation & Automation |
Leverages technology to make inventory intelligent, predictive, and self-optimizing. |
– AI/ML for demand prediction- IoT sensors for usage tracking- Digital twins for asset-linked inventory planning |
Global oil major uses digital twins to forecast spare part needs months in advance, aligning with predictive maintenance. |
The Inventory Management Challenge in Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry faces unique inventory management challenges due to the scale and complexity of operations. A typical large energy company manages approximately 800,000 spare parts SKUs across global facilities, representing inventory values ranging from millions to billions of dollars.
These organizations often struggle with 10-20% duplication in their material master databases, leading to redundant procurement, excess inventory, and operational inefficiencies.
Duplicated and Non-Standard Item Records:
Because different sites and engineers create material records locally, items often appear multiple times under different descriptions.
Example:
-
“Valve, Gate, 4in, SS316”
-
“4-inch Stainless Steel Gate Valve”
-
“Gate Valve SS 4 inch”
These could represent the same item, yet each has its own material code — leading to redundant inventory, higher carrying costs, and confusion during maintenance.
Missing or Incomplete Attributes:
Critical attributes such as pressure rating, temperature class, or API/ANSI standard are often missing.
For instance, a description like “Pump, Centrifugal” without data on flow rate, head, impeller material, or manufacturer is insufficient for maintenance or sourcing.
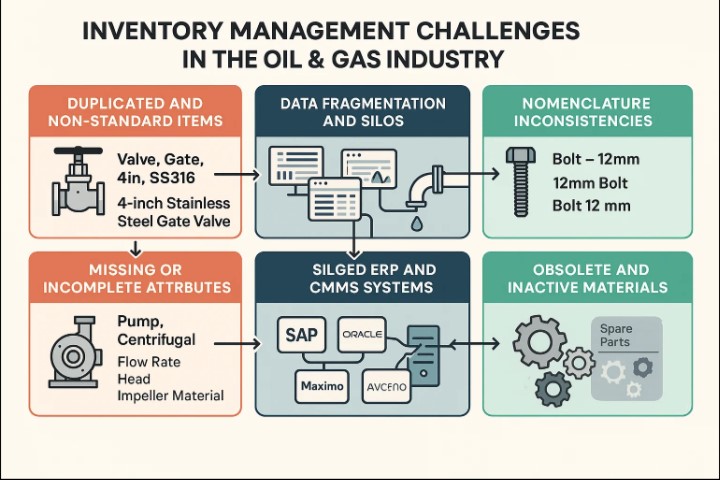
Data Fragmentation and Silos:
Legacy systems and disparate operational units create data silos that prevent comprehensive inventory visibility. Vast enterprise-wide records, siloed functional groups, and various field operations locations result in data that is “generally inaccurate, disconnected, and often becomes an operational liability”.
This fragmentation directly impacts inventory decision-making, as maintenance workers, field personnel, and procurement teams cannot work together systematically when data is inconsistent across systems.
Nomenclature Inconsistencies:
Without standardized naming conventions, the same component can appear multiple times in inventory systems with different descriptions.
For example, a simple bolt might be entered as “Bolt – 12mm,” “12mm Bolt,” or “Bolt 12 mm,” creating artificial demand signals and procurement redundancies.
These inconsistencies are often perpetuated by open text entry systems that allow employees to create multiple entries for identical parts.
Siloed ERP and CMMS Systems:
Oil and gas enterprises often run multiple ERPs (e.g., SAP, Oracle, Maximo) across different business units and geographies. Without a data layer, these systems can’t share clean, synchronized information, leading to errors in stock visibility and ordering.
Obsolete and Inactive Materials:
With equipment upgrades or process changes, thousands of spare parts become obsolete, yet remain in stock or on the books due to lack of data governance.
A major refinery in the Middle East found that over 35% of its inventory was obsolete or duplicated – worth millions in working capital.
Core Data Domains for Oil and Gas Inventory
Data_Domain | Key_Attributes | Data_Standards | Governance_Requirements |
Material Data | Item Number, Description, UNSPSC Code, Material Type, Unit of Measure, Criticality | UNSPSC Classification, ISO Standards | High – Critical for Procurement |
Asset Data | Asset Tag, Serial Number, Location, Manufacturer, Model, Criticality Rating | ISO 14224, API Standards | Very High – Safety Critical |
Supplier Data | Vendor ID, Name, Address, Qualification Status, Performance Rating | DUNS Number, ISO 9001 Certification | High – Vendor Performance |
Customer Data | Customer ID, Name, Classification, Credit Terms, Location | ISO Country Codes | Medium – Customer Relations |
Location Data | Site Code, Facility Name, Geographic Coordinates, Operational Status | Geographic Coordinates, Facility Codes | High – Operational Planning |
Well Data | API Number, Well Name, Location, Status, Production Data | API Well Numbering Standard | Very High – Regulatory Compliance |
Equipment Data | Equipment ID, Type, Specifications, Maintenance Schedule, Criticality | Equipment Classification Standards | Very High – Maintenance Planning |
Service Data | Service Code, Description, Category, Provider, SLA Terms | Service Classification Standards | Medium – Service Management |
Material Master Data:
The material master serves as the central repository for all inventory items, from consumables to critical spare parts. Essential attributes include unique item numbers, detailed descriptions, UNSPSC classification codes, material types, units of measure, and criticality ratings.
The UNSPSC provides standardized commodity classification, with specific segments relevant to petroleum operations including Segment 15000000 (Fuels and Fuel Additives), Segment 20000000 (Mining and Well Drilling Machinery), and Segment 40000000 (Distribution and Conditioning Systems).
Asset Master Data:
Physical assets require comprehensive master data encompassing asset tags, serial numbers, location hierarchies, manufacturer information, model specifications, and criticality ratings. This data directly supports maintenance planning and spare parts optimization by establishing relationships between equipment and required inventory items.
Supplier Master Data:
Vendor information must include supplier identification numbers, qualification statuses, performance ratings, and lead time data to support procurement optimization.
In the oil and gas sector, supplier master data often incorporates specialized certifications and regulatory compliance status essential for safety-critical operations
Oil and Gas Inventory Management Process
MDM creates a centralized, governed framework for managing all material and supplier data across the enterprise.
Using international standards such as UNSPSC, ISO 14224 (for equipment reliability data), or API RP 581, MDM ensures uniform naming and classification across all locations.
For example:
A “Ball Valve” might be represented consistently as:
Valve, Ball, Carbon Steel, 4 Inch, 600 LB, Flanged End, API 6D.
This structured format ensures every engineer, buyer, or maintenance planner understands exactly what the item is, regardless of site or language.
MDM platforms employ fuzzy matching and AI algorithms to identify duplicates based on text similarity, supplier names, and attribute values.
Example: A North Sea operator discovered 12,000 duplicate material codes after harmonization – enabling a 15% reduction in total inventory value and freeing up storage space on offshore rigs.
A central MDM hub integrates with all ERP, CMMS, and EAM systems across the enterprise – ensuring one source of truth for every material record.
This integration ensures that when a new “Pump Seal Kit” is created in one refinery, it’s instantly visible and reusable in others.
By integrating with manufacturer catalogs and engineering databases, MDM enriches records with detailed technical attributes such as:
- Pressure and temperature ratings
- Material specification (e.g., ASTM A105, A182 F316)
- OEM part numbers
- Certification data (e.g., API, NACE compliance)
This allows accurate part identification, sourcing of alternatives, and compatibility analysis during maintenance shutdowns.
Automated workflows enforce naming conventions, approval hierarchies, and change management processes.
New materials cannot be created without proper attribute completion, classification, and validation – reducing future duplication and data drift.
Industry Standards and Classification Systems
The oil and gas industry relies on several standardized classification systems to ensure consistent data management. The API (American Petroleum Institute) Well Numbering Standard provides unique identification for petroleum wells in the USA, utilizing a 12-digit format that includes state codes, county codes, sequence codes, and wellbore codes.
This standard, maintained by the Professional Petroleum Data Management (PPDM) Association since 2010, ensures comprehensive data management essential for regulation, operation, and evaluation of wells.
UNSPSC_Code | Category_Name | Application_Area | Data_Complexity |
15000000 | Fuels and Fuel Additives | Downstream Operations | Medium |
15101506 | Gasoline or Petrol | Retail/Distribution | Low |
20000000 | Mining and Well Drilling Machinery | Upstream Operations | High |
20101805 | Ground Support System Spare Parts | Upstream Support | High |
26000000 | Power Generation Equipment | Power Generation | High |
40141600 | Valves | Process Equipment | Medium |
40161500 | Filters | Process Equipment | Medium |
23111600 | Petroleum Distilling Equipment | Refining Operations | High |
31000000 | Manufacturing Components | General Manufacturing | Medium |
39000000 | Electrical Systems | Electrical Infrastructure | Medium |
UNSPSC Classification Implementation: The United Nations Standard Products and Services Code provides hierarchical commodity classification essential for procurement standardization. For oil and gas operations, key UNSPSC segments include:
15000000: Fuels, Fuel Additives, Lubricants, Anti-corrosive Materials
20000000: Mining and Well Drilling Machinery and Accessories
23000000: Industrial Manufacturing and Processing Machinery
26000000: Power Generation and Distribution Machinery
40000000: Distribution and Conditioning Systems and Equipment
These codes enable consistent material classification across global operations, supporting strategic sourcing initiatives and spend analytics.
Data Quality Issues and Solutions
The complexity of oil and gas operations creates numerous data quality challenges that directly impact inventory management effectiveness.
Research indicates that organizations typically experience 15-30% data accuracy issues due to manual data entry processes, while 43% of small businesses operate without proper inventory tracking systems
AI-Powered Data Cleansing:
Modern MDM solutions leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to address data quality issues systematically.
AI-based deduplication can achieve 75% reduction in duplicate records, while automated data enrichment processes ensure 80% complete technical specifications across material databases.
Verdantis’ data management solution, for example, enabled a major Middle Eastern utility to reduce spare parts redundancies by 15%, delivering $3.2 million in annual savings.
Standardization Through Governance:
Effective data governance frameworks establish policies, standards, and business rules that ensure data consistency across the organization.
The Data Governance Institute (DGI) framework emphasizes four key components: value statements and metrics, data rules and decision rights, controls and standards, and people and processes. In oil and gas contexts, these frameworks must address regulatory compliance requirements while supporting operational efficiency objectives.
Technical Impact of Inventory on Oil & Gas Operations
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems serve as the primary platform for inventory data management in large oil and gas organizations, with SAP S/4HANA and Oracle EBS achieving adoption rates exceeding 85% in the industry.
These platforms provide centralized data repositories that break down organizational silos and create unified sources of truth for inventory management.
Platform_Type | Leading_Solutions | Oil_Gas_Adoption | Implementation_Complexity |
ERP Systems | SAP S/4HANA, Oracle EBS | Very High – 85%+ | High |
MDM Platforms | Profisee, Informatica MDM, SAP MDM | Medium – 45% | Very High |
Data Quality Tools | Talend, Informatica Data Quality | Growing – 35% | Medium |
Integration Tools | MuleSoft, Dell Boomi | High – 60% | Medium |
Analytics Platforms | Tableau, Power BI, SAP Analytics | High – 70% | Medium |
Governance Tools | Collibra, Alation | Growing – 25% | High |
SAP Implementation in Oil and Gas:
Major petroleum companies have successfully implemented comprehensive SAP-based solutions, Business Intelligence, Process Integration, and Master Data Management modules.
Verdantis’ implementation for a major oil and gas company automated key business processes including logistics (procurement, sales and distribution, warehouse operations), equipment maintenance and repair, and organizational management across seventeen branches simultaneously.
Cloud-Based MDM Solutions:
Modern cloud-based platforms like SAP S/4HANA Cloud offer real-time data integration capabilities essential for dynamic inventory management. These solutions support the “golden record” approach to data management, ensuring consistency and reliability across all datasets while enabling scalable operations
Area | MDM Application | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Procurement | Consolidation of supplier and material data | Reduces maverick buying and improves contract compliance |
Maintenance & Reliability | Attribute-rich parts data linked to asset hierarchies (e.g., API 610 pumps) | Faster MTTR (Mean Time to Repair) and reduced unplanned downtime |
Inventory Optimization | Identification of duplicates, obsolete, and slow-moving items | Lowers working capital and improves warehouse utilization |
Engineering Projects | Unified bill of materials and component data | Speeds up project handover and commissioning |
Safety & Compliance | Complete traceability for hazardous materials | Ensures regulatory compliance (EPA, OSHA, ISO 45001) |
Governance Frameworks and Best Practices
Successful master data management in oil and gas requires comprehensive governance frameworks that address the industry’s unique regulatory and operational requirements. The (DMBoK) provides foundational principles, while industry-specific frameworks address petroleum sector challenges.
Critical Data Elements (CDEs): Data governance initiatives must identify and prioritize Critical Data Elements that have the greatest impact on business operations.
In oil and gas contexts, CDEs typically include safety-critical equipment specifications, environmental compliance data, and production-critical spare parts information. This prioritization ensures that limited resources are directed toward maintaining accuracy and reliability of the most essential data elements.
Enterprise Data Governance Framework: Leading oil and gas companies implement structured governance approaches that combine data strategy, data quality management, and data management.
These frameworks establish clear roles and responsibilities for data ownership and stewardship while defining processes for data lifecycle management from collection through disposal.
Integration with Inventory Optimization
Data quality directly impacts inventory optimization outcomes, with poor data governance having demonstrated negative effects on corporate performance in petroleum operations.
Effective MDM enables advanced analytics and machine learning technologies that support predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and strategic procurement.
Criticality-Based Classification: MDM systems support sophisticated criticality analysis frameworks like ABC-VED-Criticality models that categorize inventory based on value, criticality, and usage frequency. This classification enables focused resource allocation, with A-items receiving tight control, B-items scheduled review, and C-items bulk purchasing or consignment arrangements.
Real-Time Integration: Modern MDM platforms integrate with warehouse management systems (WMS), enterprise asset management (EAM), and supply chain management (SCM) systems to provide real-time inventory visibility.
This integration supports dynamic reorder level optimization and minimum-maximum policy implementation with predictive analytics capabilities.
Real-World Example: Refinery Material Harmonization
A large integrated oil company managing over 400,000 material records across its upstream and downstream operations faced severe inefficiencies:
22% duplicate items
Inconsistent taxonomies across six ERPs
No visibility into stock commonality across plants
After implementing a centralized MDM system:
All material data was classified under UNSPSC and ISO 14224 frameworks.
Duplicate entries (e.g., fasteners, gaskets, valves) were consolidated using AI matching.
Missing data such as material composition, pressure class, and part manufacturer was automatically enriched.
Results:
Inventory value reduced by 18% due to elimination of duplicates.
Search time for maintenance parts improved by 45%.
Procurement achieved 5–8% savings through vendor consolidation and improved spend analysis
Verdantis MRO data cleansing enterprise software’s enable clients across various asset-intensive industries to achieve significant operational improvements.
- Optimized Inventory Management: Eliminates duplicate/obsolete parts, reduces inventory bloat and carrying costs, ensuring optimal stock levels.
- Enhanced Maintenance Planning & Asset Reliability: Standardizes MRO data for accurate work orders and BOMs, leading to effective preventive maintenance and reduced downtime.
- Improved Procurement Efficiency & Cost Reduction: Enables better vendor rationalization and visibility, preventing redundant purchases and securing cost savings.
- Successful ERP/EAM Implementations & Digital Transformation: Provides clean MRO master data for smoother system migrations, better adoption, and reliable analytics.
- Robust Data Governance & Compliance: Establishes clear data standards, real-time workflows, and audit trails for ongoing data quality and reduced compliance risks.
- Streamlined Operations across Functions: Creates a single source of truth for MRO data, improving cross-functional collaboration and efficiency.
Verdantis’ enterprise software suite helps global organizations cleanse, enrich, and govern their MRO and indirect material data at scale. Deployed across complex ERP and EAM ecosystems, Verdantis AutoEnrich AI, AutoClass AI, AutoTrans AI, and Integrity enable measurable value across multiple industries.
Future Trends and Digital Transformation
The oil and gas industry’s inventory data management practices continue evolving through digital transformation initiatives that leverage emerging technologies. Digital transformation economic impact is projected to reach $1.6 trillion USD by 2030, with master data management serving as a critical enabler.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-powered MDM solutions provide automated data classification, enrichment, and validation capabilities that significantly reduce manual effort while improving data accuracy. Verdantis platform utilizes agentic AI to cleanse, enrich, and organize master data automatically, supporting continuous improvement in data quality.
Blockchain and Data Integrity: Emerging blockchain technologies offer potential solutions for ensuring data integrity and provenance across complex oil and gas supply chains. These technologies could provide immutable records of data changes, supporting regulatory compliance and audit requirements while enabling trusted data sharing across industry partnerships.
The integration of robust data management practices with inventory optimization represents a strategic imperative for oil and gas organizations seeking to maximize operational efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain competitive advantage in an increasingly complex and data-driven industry environment.





