Organizations are continually seeking to harness technology to enhance efficiency, automation, and data-driven decision-making. Among these advancements, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become the foundation of business operations, enabling seamless integration across finance, procurement, supply chain, manufacturing, HR, and other key functions.
However, the success of an ERP system largely hinges on a crucial element—Master Data Management (MDM). Inaccurate or poor-quality data can lead to inefficiencies, compliance challenges, and costly errors. This article delves into the importance of ERP Master Data Management, best practices for maintaining high-quality data, and how AI-powered platforms like Verdantis are transforming this space.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become indispensable tools for modern businesses seeking to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage. These systems integrate various business functions, such as finance, manufacturing, and distribution, into a unified platform, enabling better resource management.
Understanding ERP Master Data
Master data refers to the core business information that remains relatively stable over time and is referenced by various business processes within an ERP system.
An ERP system acts as a central hub, connecting disparate business functions into a cohesive whole. It comprises various modules, each catering to specific organizational needs.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software packages are integrated packages of software used by firms to administer and automate business functions—finance, human resources, procurement, logistics, supply chain, etc. There is a particular form of data called Master Data within an ERP package. Master Data is the fundamental data which is modified relatively less over time and is utilized by the functional departments of the firm.
An ERP system is often the primary hub for Master Data. However, in complex organizations with multiple systems (like CRM, PLM, and specialized tools), a central MDM strategy coordinates Master Data across all these platforms.
Example:
- A company has a CRM system for sales team interactions with customers.
- The ERP system handles order processing, inventory, and financials.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software suite that integrates various business functions into a single system.
It facilitates seamless communication across different departments, ensuring real-time data access and enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions.
Based on industries, the most important Master Data categories for each industry are:
1. Material Master Data
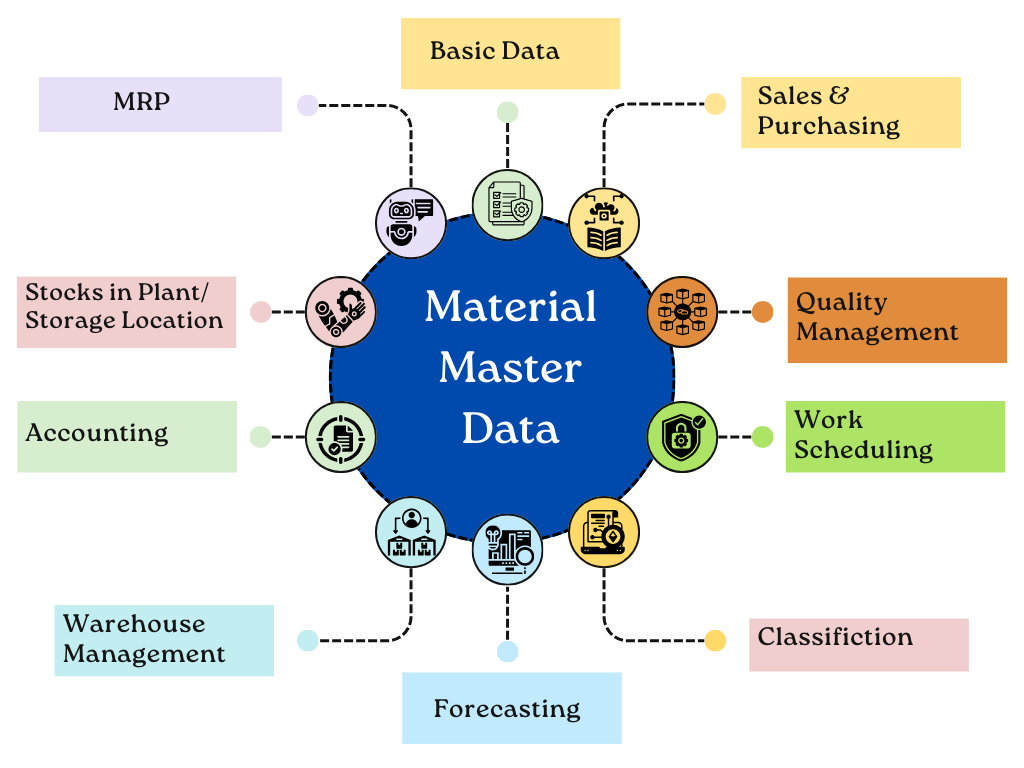
Material Master Data is a critical foundation of ERP systems, supporting supply chain, procurement, and inventory management. It tracks material descriptions, identification numbers, specifications, procurement details, supplier information, storage locations, pricing, batch numbers, expiry dates, and compliance requirements. A well-structured Material Master Data system ensures seamless integration across procurement, manufacturing, sales, and logistics, improving inventory tracking, demand forecasting, cost analysis, and regulatory compliance.
Despite its importance, managing Material Master Data presents challenges like data duplication, non-standard naming conventions, lack of standardization, and outdated records. These inefficiencies cause procurement delays, production bottlenecks, incorrect inventory levels, and increased operational costs.
Poor data quality misaligns supply chain activities and increases compliance risks, making strong data governance essential. Standardized naming conventions, automated data cleansing, and AI-driven validation improve data quality and efficiency.
AI-powered platforms like Verdantis are transforming Material Master Data Management by eliminating duplicates, harmonizing data across ERP systems, and enhancing accuracy through automation and machine learning. These solutions reduce procurement and inventory costs, minimize supply chain disruptions, and enable data-driven decision-making. By prioritizing high-quality Material Master Data, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and maintain a competitive edge.
Example: A food and Beverage company maintains Ingredient Name, Batch ID, Allergen Information, Expiry Date, Nutritional Values, and Packaging Details to comply with food safety regulations and ensure product quality.
Discover more about our specialized Material Master Data solutions by visiting our dedicated page
2. Customer Master Data
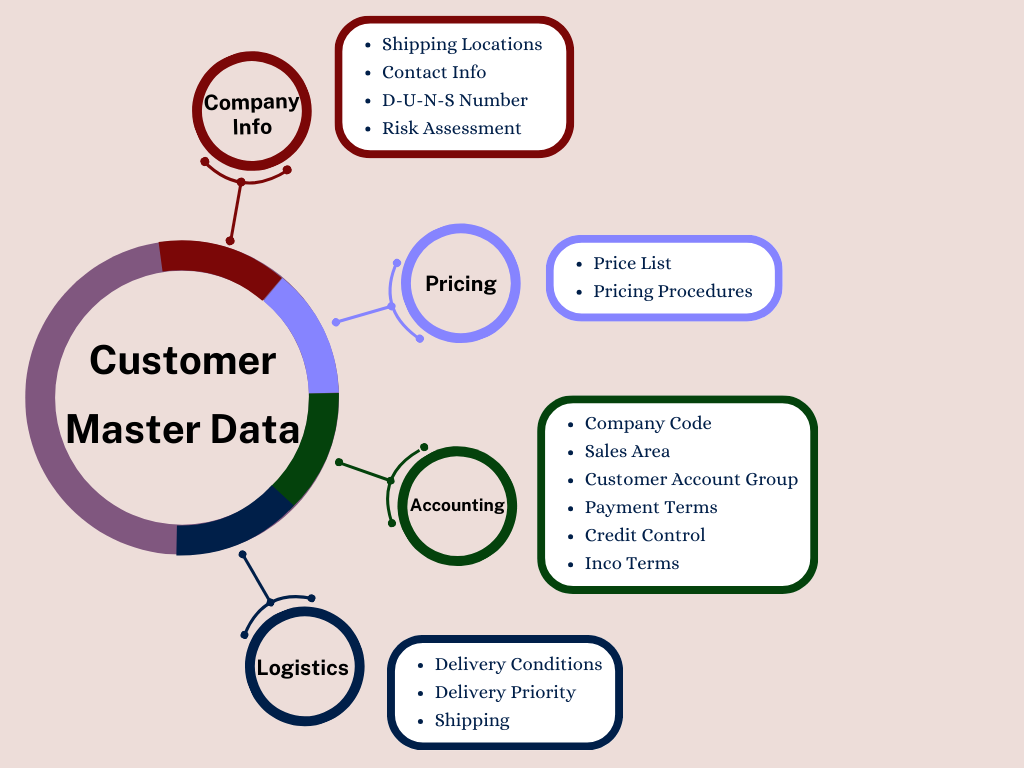
Customer Master Data Management is essential for enterprises to maintain accurate, unified, and structured customer records. It supports key functions like sales, marketing, finance, and customer service. Poorly managed customer data leads to inefficiencies, lost revenue, compliance risks, and poor customer experiences.
With digital transformation, businesses must adopt a structured, real-time, and accessible approach to managing customer data. A well-maintained customer master enables accurate reporting, streamlined operations, personalized customer experiences, and improved regulatory compliance, ultimately driving better customer relations and increased revenue.
Customer Master Data includes essential attributes such as customer IDs, names, addresses, contact details, tax identification numbers, credit limits, and payment terms. It also contains sales and marketing data like purchase history, segmentation, and loyalty programs, as well as customer service records such as support tickets and feedback history.
ERP systems heavily rely on high-quality Customer Master Data to ensure a seamless flow of information across departments. Maintaining a single source of truth improves coordination between sales, marketing, and customer service teams, enhances CRM efforts, and enables finance teams to process transactions accurately. It also helps businesses comply with tax regulations, data privacy laws, and industry-specific requirements.
However, managing Customer Master Data comes with challenges like data duplication, inconsistent records, manual entry errors, lack of governance, and integration issues between ERP, CRM, and other enterprise systems. Businesses must implement a structured approach, including centralized data repositories, standardized data governance policies, AI-driven data cleansing tools, and seamless ERP-CRM integration.
Regular data audits and cleansing processes help maintain data integrity. Predictive analytics enables deeper insights into customer behavior and trends, facilitating personalized engagement and informed decision-making. Platforms like Verdantis ensure regulatory compliance and reduce financial and legal risks by maintaining high-quality customer data.
Example: An e-commerce retailer maintains customer records, including Customer ID, Name, Address, Contact Number, and Email, to tailor marketing campaigns and send order confirmations.
Discover more about our specialized Customer Master Data solutions by visiting our dedicated page
3. Supplier/ Vendor Master Data
Supplier/Vendor Master Data is an essential element in procurement and supply chain management, providing a centralized repository of essential supplier information. The details include basic supplier names, contact information, financial records, product and service offerings, compliance certifications, and performance metrics.
Proper Supplier Master Data is crucial for the seamless working of the ERP system; this ensures proper processing of purchase orders, payment accuracy, contract management, and monitoring of the supplier’s performance.
However, organizations suffer from data duplication, inconsistencies, outdated records, lack of standardization, and integration challenges across multiple systems. Poor-quality supplier data can cause procurement inefficiencies, financial losses, and compliance risks.
In order to counter these issues, businesses must implement best practices that include centralized data governance, standardized data formats, automated data cleansing, and integration across ERP, procurement, and financial systems. This article talks about the best practices for vendor master data.
The following are further enhancement of data accuracy and efficiency through regular audits and self-service portals for suppliers. AI-driven platforms like Verdantis are transforming the way Supplier Master Data Management works by automating data deduplication, enrichment, and validation, thus enabling real-time visibility and compliance.
AI and machine learning can thus be leveraged to optimize supplier relationships, reduce procurement risks, and drive cost efficiencies. Ultimately, well-structured and high-quality Supplier Master Data is no longer only a necessity but a strategic enabler that supports operational agility and data-driven decision making within modern enterprises.
Example: A manufacturing firm maintains Vendor ID, Company Name, Address, Contact Details, Payment Terms, Tax ID, and Banking Information to streamline procurement, ensure timely payments, and track supplier performance.
Discover more about our specialized Vendor Master Data solutions by visiting our dedicated page
4. Employee Master Data
Employee Master Data is the foundation dataset that has all the crucial employee-related information in an organization’s Human Resource Management (HRM) and ERP systems. It is, therefore, the single source of truth for all employee records with the aim of maintaining consistency, accuracy, and compliance across multiple HR functions.
This data typically includes personal details (name, date of birth, contact information, identification numbers), employment-related information (job title, department, designation, reporting structure, hire date, employment status), payroll and compensation details (salary structure, tax deductions, benefits, bonuses), and performance-related records (appraisals, training history, certifications).
Managing Employee Master Data effectively is crucial for seamless HR operations, including payroll processing, performance evaluations, compliance tracking, workforce planning, and employee engagement. However, issues in data redundancy, inconsistency, and security can develop when dealing with employee records managed across departments, locations, or business units.
Organizations develop their data governance framework, role-based access controls, and AI-powered automation tools that validate, clean, and standardize employee master data to manage these risks. With correct employee master data, companies improve efficiency in their workforces, effective decision-making, compliance with rules, and streamline the experience for employees.
Example: A production facility maintains Employee ID, Skill Proficiency Levels, Safety Training Records, Shift Assignments, Overtime Tracking, and Equipment Handling Certifications to optimize workforce management, ensure compliance with safety regulations, and enhance operational efficiency.
Discover more about our specialized Employee Master Data solutions by visiting our dedicated page
5. Product Master Data
Product Master Data is a collection of all product-related attributes and information that rests in the master database in any given ERP system. Product Master Data is a centralized dataset that contains detailed and structured information about a company’s products or services. It serves as the single source of truth for product-related data across various business functions such as sales, procurement, inventory management, manufacturing, and customer service.
Product Master Data typically includes attributes like product name, SKU (Stock Keeping Unit), descriptions, specifications, pricing, unit of measure, category, supplier details, compliance certifications, and lifecycle status. A product master helps provide a unified view of all product-related information and ensures consistent information across CRM (Customer Relationship Management), ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and PIM (Product Information Management) systems in the organization.
As organizations scaled, a high volume of product data was generated across different departments and silos. Quite often, gaps in various processes and an absence of data management and governance practices led to “dilution” or “contamination” of this product data.
Thus, the need for a centrally managed product master database became immediately apparent among leading enterprises worldwide and major ERPs began developing out of the box solutions for PMDM within their offerings.
For example; SAP launched PMDM, a set of features that can help with product development and change processes, and similarly other vendors that launched their MDM tools to help businesses implement the master data management solutions, including product master data as one of the data domains. It helps centrally manage and govern product-related data and integrate the same across internal and external systems.
Example: A manufacturing company maintains Product Code, Material Composition, Bill of Materials (BOM), Production Specifications, Unit of Measurement, Warranty Period, and Compliance Certifications to ensure standardized production, monitor product lifecycles, and adhere to regulatory requirements
Discover more about our specialized Product Master Data solutions by visiting our dedicated page
Discover how Verdantis’ AI-powered solutions can optimize data governance, enhance compliance, and drive operational efficiency.






6. Finance Master Data
Financial Master Data is the fundamental data used for all financial transactions, reports, and compliance processes in an organization. Financial Master Data acts as a source of truth for essential financial elements across various business functions, providing consistency, accuracy, and compliance with regulations.
Financial master data is normally comprised of major entities such as a chart of accounts, cost centers, profit centers, general ledger accounts, tax codes, bank details, currency exchange rates, and financial hierarchies, central for budgeting, financial planning, invoicing, taxation, and financial reporting.
Financial Master Data is core data that serves as the backbone of an organization’s financial transactions, accounting processes, and reporting structures. It is a single source of truth for financial elements across all business operations, thus ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and regulatory compliance. All financial transactions within an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system depend on well-structured Financial Master Data, making it one of the most critical components of business data management.
Maintaining clean and well-structured Financial Master Data is crucial for accurate financial reporting, streamlined audits, compliance with regulations (such as IFRS, GAAP, and SOX), and effective decision-making. Poor financial data quality can lead to errors in financial statements, miscalculations in tax filings, and inefficiencies in financial consolidation. Organizations often leverage ERP systems with robust Financial Master Data Management capabilities to ensure data accuracy, eliminate redundancies, and improve financial governance.
Example: A company maintains General Ledger Codes, Chart of Accounts, Cost Centers, Tax Identification Numbers, Bank Account Details, Payment Terms, and Currency Codes to ensure precise financial reporting, streamline transactions, adhere to tax regulations, and optimize budget management across various departments.
What is Master Data in ERP?
Master data refers to the core business information that is used across multiple functions within an organization. It serves as the foundation upon which an ERP system operates.
Master data typically includes:
Customers: Name, contact details, credit terms, payment preferences.
Vendors/Suppliers: Business information, bank details, tax identification.
Materials/Products: Product descriptions, pricing, SKU numbers, inventory levels.
Employees: Personal details, job roles, payroll information.
Financial Data: Chart of accounts, cost centres, tax codes.
Master data is not transactional data but provides the essential reference points that all ERP transactions rely on.
Key ERP Modules That Rely on Master Data
- Finance & Accounting – Requires accurate financial master data for reporting, compliance, and budgeting.
Procurement & Supply Chain – Vendor and material master data play a crucial role in supplier management and inventory optimization.
Manufacturing & Production – Relies on structured material master data for bill of materials (BOM) and production planning.
Human Resources (HR) – Needs clean employee master data for payroll, benefits, and workforce planning.
Plant Maintenance: Tracks and manages maintenance activities for equipment and facilities.
Quality Management: Ensures product quality through inspections, testing, and quality control processes.
A key characteristic of an ERP system is its integrated nature. Modules are interconnected, allowing seamless information flow across departments.
This integration is facilitated by shared databases and, crucially, master tables. These master tables contain the foundational data that is repeatedly used throughout the system, supporting various applications, functional areas, and even different geographical locations.
Master Data Management (MDM) in ERP
Master Data Management (MDM) is the discipline and technology used to create and maintain a single, accurate, and consistent view of an organization’s master data. It involves establishing processes, policies, and technologies to ensure data quality, consistency, and accessibility across the enterprise. Effective MDM is crucial for maximizing the value of an ERP system.
These systems rely on master data to create a single source of truth, eliminating data silos and inconsistencies across different modules.
📘 Key components of MDM in ERP include:
Data Governance: Establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing master data. This includes defining data ownership, data stewardship, and data quality rules.
Data Quality Management: Implementing processes and tools to cleanse, standardize, and validate master data. This includes identifying and correcting errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies.
Data Integration: Integrating master data from various sources into a central repository. This ensures a single source of truth for master data across the organization.
Data Modelling: Defining the structure and relationships of master data elements. This ensures consistency and facilitates data sharing across the enterprise.
Data Security: Implementing security measures to protect
Challenges in ERP Master Data Management
Many organizations struggle with maintaining clean and accurate master data in their ERP systems. Some common challenges include:
Data Inconsistencies Across Business Functions – Different departments maintain their own versions of data, leading to mismatched records.
Duplicate and Redundant Data – Without proper governance, multiple entries for the same vendor, material, or customer can exist.
Lack of Standardization – Different naming conventions, formats, and incomplete data make it difficult to use data effectively.
Impact on Business Performance – Poor data quality results in operational inefficiencies, financial discrepancies, and inaccurate business reporting.
Best Practices for Effective ERP Master Data Management
We have discussed some of the best practices to implement ERP Master Data Governance, similarly, their are strategies that companies can adopt to effectively implement ERP master data management:
Establishing Data Governance Policies
Set and define ownership on data, the responsibility for owning it, who is responsible.
Set up standard operating procedures for data entry and maintenance.
Ensuring Data Accuracy, Completeness, and Consistency
Validate and standardize master data before entering it into the ERP.
Implement rules for naming conventions and data structures.
Implementing AI-Driven Data Cleansing and Enrichment
- Leverage AI to detect and correct errors in master data.
- Use machine learning models to identify and remove duplicates.
Regular Data Audits and
Quality Checks
- Periodically review and cleanse master data.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory and internal data governance policies.
The Role of Automation in MDM
Automate data validation and cleansing processes.
Use AI-based tools to enrich and classify master data dynamically.
The Importance of Data Migration in ERP Master Data Management
Big industry giants and organizations are increasingly relying on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to streamline operations, reduce cost, and improve decision-making.
Nevertheless, the real value of an ERP system is only possible if the information input into it is correct, up-to-date, and consistent.
This is the best example of the absolute need for data migration in the case of ERP Master Data Management (MDM), especially material master data, as the foundation of procurement, inventory management, and production processes.
Data migration is the act of moving data from a source system to a destination system, such as moving data from legacy systems or the outside world into a new ERP system.
The activity is central to the success of an ERP implementation since the accuracy, quality, and completeness of the data moved will impact the success of the ERP solution.
1. Ensuring Data Quality and Integrity
One of the most important reasons for spending time and money on data migration is to make sure that the data in the ERP system is of good quality. ERP systems depend very much on good data for major processes like order fulfillment, procurement, production planning, and financial reporting. If the data in the system is wrong, inconsistent, or incomplete, it can cause problems like:
Incorrect financial reports
Inefficient inventory management
Miscommunication between departments
Delays in production cycles
Data cleansing, an integral part of data migration, addresses these problems by locating and fixing inaccuracies in the data prior to its entry into the new ERP system. By removing duplicates, normalizing formats, and completing missing information, businesses can make sure that only correct, consistent, and pertinent data is transferred.
2. Improving Operational Efficiency
Effective data migration enhances operational effectiveness through the guarantee of employees using the right and latest data. For material master data, this implies that procurement departments will be using precise details about suppliers, materials, and inventories.
Production departments will enjoy timely access to information about bill of materials (BOM) and part details, minimizing chances of mistakes and delays.
A successful migration enables organizations to remove redundant or obsolete data so that only the most actionable and relevant data is retained in the ERP system. The decluttering of this sort reduces teams’ efforts in focusing on value-added activities, and decision-making becomes improved with more streamlined day-to-day operations.
3. Facilitating Compliance and Data Governance
Data governance is a key feature of ERP Master Data Management, and data migration is the initial step to ensure that the data in the ERP system follows organizational and regulatory requirements. Master data, and specifically material master data, is strictly regulated in a number of industries, such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and food & beverage.
Moving data into the ERP system with inherent governance guarantees that the system will be in compliance with regulatory requirements, e.g., industry certifications or internal controls. This will prevent legal or monetary fines as a result of non-compliance and ensure a solid audit trail.
Data governance also guarantees that material master data remains accurate, consistent, and secure across departments, minimizing data silos and ensuring cross-functional collaboration.
4. Supporting Digital Transformation and Scalability
As organizations undergo digital transformation, they seek to modernize their technology infrastructure and enhance the scalability of their operations. A smooth data migration process is crucial for ensuring that ERP systems can effectively support this transformation.
By ensuring that data is well-structured and cleansed prior to migration, organizations can improve the long-term performance of their ERP system.
Having clean and organized data enables businesses to scale operations more effectively as demand increases. For instance, if a company plans to expand into new markets, introduce new product lines, or merge with other businesses, a solid data foundation will facilitate the seamless integration of new business models, vendors, and supply chains into the ERP system without causing disruptions.
Data Migration from SAP ECC TO S/4 HANA
Migrating from SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) to SAP S/4HANA is a huge change for companies, as they are shifting from an old-style ERP system to a next-generation, intelligent enterprise suite based on SAP HANA.
SAP S/4HANA is a streamlined, real-time platform that combines fundamental business processes with sophisticated features such as AI, machine learning, and predictive analytics. The move to S/4HANA enables companies to:
Streamline operations: The system has a simple data model and user interface that minimizes the complexity of operations.
Improve performance: Backed by the SAP HANA in-memory database, S/4HANA offers quicker processing times and real-time analytics.
Enhance flexibility: It provides higher flexibility with deployment choices, including on-premise, cloud, or hybrid options.
Drive innovation: The system allows companies to take advantage of cutting-edge technologies such as IoT, automation, and artificial intelligence, making it simpler to innovate and remain competitive in a digital-first economy.
For companies that are migrating to S/4HANA, this transition not only updates their technology stack but also brings their operations in line with the future of business management.
ERP Agnostic Solutions
Seamless out-of-the-box OR custom integration with all major ERPs
SAP
Native integration with S4/Hana & SAP Business One
INFOR
Custom integration for Integrity & Harmonize
Oracle
Native integration with JD Edwards & NetSuite
ODOO
Custom integration for Integrity & Harmonize
How AI is Transforming ERP Master Data Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is redefining how businesses manage their ERP master data. Key advancements include:
AI-Powered Data Cleansing and Enrichment: By automatically detecting and correcting discrepancies, AI technologies minimize human labor.
Improving Data Accuracy Through Machine Learning: AI models are always learning from patterns, which increases data dependability.
Predictive analytics for proactive data management: AI ensures data quality by anticipating problems before they happen.
Case Study: Verdantis’ Use of AI to Transform MDM For the past 20 years, Verdantis has led the way in AI-driven data enrichment and purification, assisting businesses in streamlining their ERP data.
Integrate Master Data from All Sources: Integrate master data from various systems into a central repository to create a single source of truth.
Train Employees on Data Management Best Practices: Provide training to employees on data entry, data quality, and data governance procedures.
Monitor Data Quality Regularly: Regularly monitor data quality metrics to identify and address data issues proactively.
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define KPIs to measure the effectiveness of MDM initiatives and track progress over time.
Future Trends in ERP Master Data Management
The field of ERP MDM is constantly evolving. Some key trends to watch include:
Cloud-Based MDM: Increasing adoption of cloud-based MDM solutions, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Leveraging AI and ML to automate data cleansing, data matching, and data governance tasks.
Data as a Service (DaaS): Utilizing DaaS providers for access to high-quality master data.
Focus on Data Security and Privacy: Increased emphasis on data security and privacy regulations, such as GDPR, in MDM initiatives.
Real-Time Data Management: Moving towards real-time data management to support agile business processes and decision-making.





