MRO (Maintenance, Repair, and Operations) data refers to master data for indirect materials like spare parts, consumables, and equipment used to maintain assets and facilities. Unlike direct production materials, MRO items are often inconsistently named, poorly classified, or missing key specifications. This creates excess inventory, inefficiencies, and unplanned maintenance disruptions.
Clean and standardized MRO data is essential for asset-heavy industries. Poor-quality data can result in:
Duplicate orders
Inaccurate inventory records
Poor maintenance planning
Compliance risks
Organizations often struggle with fragmented MRO data due to:
Mergers and acquisitions
Multiple ERP and legacy systems
Distributed plants with diverse equipment and histories
At a broader level, MRO cleansing is a critical component of enterprise Master Data Cleansing, ensuring consistency not just within maintenance and operations but across procurement, finance, and supply chain systems.
By embedding data governance practices into the materials domain, organizations can drive enterprise-wide efficiency, reduce risk, and improve decision-making across the asset lifecycle.
What is MRO Data Cleansing?
MRO data cleansing is the process of correcting, standardizing, enriching, and classifying material master data to ensure that all spare parts and indirect items are accurately represented across ERP, EAM, and CMMS platforms. It involves normalization, duplicate elimination, and attribute enrichment using standardized taxonomies (e.g., UNSPSC, ECLASS, PIDX).
When executed well, MRO data cleansing and standardization services reduce inventory bloat, eliminate duplicate items, and support accurate maintenance planning.
A comprehensive MRO material cleansing process goes beyond just cleaning entries. It includes:
- MRO data normalization to standardize units and formats
- MRO data scrubbing to remove duplicate or outdated records.
- MRO data enrichment with OEM specs, attributes, and reference data
- MRO deduplication – Level-2 (L2) deduplication after enrichment to eliminate residual duplicates and ensure data uniqueness across the material master.
- MRO material master data management and classification using global taxonomies

Need For MRO Data Cleansing and Standardization Services
Accurate, standardized MRO data cataloging is critical for asset-intensive industries, yet many face issues from fragmented, outdated records. Here’s why MRO data cleansing is essential for operational and business success:
Mergers and acquisitions bring together organizations with differing ERP systems, taxonomies, and master data practices. Without proper data harmonization, M&A integrations face:
- Inflated inventories due to undetected duplicate parts
- Poor spend visibility across merged entities
- Conflicting MRO classifications or part specifications across systems
- High effort and risk in combining legacy catalogs or vendor databases
Cleansing and unifying MRO data across acquired entities is critical to achieving the promised synergies of M&A, particularly in procurement and operations.
When organizations upgrade to modern ERP or EAM platforms such as SAP S/4HANA, Oracle Cloud, or IBM Maximo, they face a critical data challenge: garbage in, garbage out.
Poor-quality MRO data in the legacy system leads to:
- Failed data migration or increased migration costs
- Poor system adoption post go-live due to unreliable search and reporting
- Breakdowns in transactional processes like purchase requisitions or work order creation
- Missed opportunities for automation, analytics, and AI-based maintenance strategies
CMMS or EAM systems depend on accurate material masters to link equipment, work orders, and spare parts.
Dirty data leads to:
- Missed preventive maintenance due to incorrect BOMs
- Equipment failures from the use of wrong or incompatible parts
- Poor reliability metrics and increased unplanned downtime
Clean MRO data supports condition-based maintenance and better asset reliability.
Procurement teams rely on accurate item data to negotiate, consolidate, and forecast purchases.
Dirty data causes:
- Redundant ordering of parts already in stock
- Inability to identify demand aggregation opportunities
- High spot-buying costs and missed discounts
Clean data enables smarter sourcing strategies and supplier collaboration.
Accurate MRO data is vital for efficient, uninterrupted industrial operations. At Verdantis, we understand that outdated or inconsistent data leads to excess inventory, duplicate purchases, costly downtime, and poor system performance.
Without proper cleansing, MRO data undermines ERP and EAM systems like SAP S/4HANA, Oracle, or Maximo. – putting digital transformation, compliance, and safety at risk.
MRO data cleansing companies like Verdantis address these challenges by providing AI-powered platforms that cleanse, classify, enrich, and govern MRO data at scale, ensuring that critical business systems operate on a foundation of trusted information.
According to Gartner, companies lose around $12.9 million annually due to general poor data quality-many of which concern MRO master and inventory data.
Industries & Roles That Depend on MRO Data Cleansing
Accurate and standardized MRO data is mission-critical in asset-intensive sectors where unplanned downtime, excess inventory, and inefficient maintenance can cost millions. Organizations across the following industries consistently rely on MRO data cleansing to drive operational excellence:
Key Stakeholders in MRO Data Cleansing
Clean, standardized MRO data is more than just a back-end improvement- it’s a frontline enabler. The following roles are central to maintenance, procurement, and operations, and rely heavily on accurate data to reduce downtime, control costs, and drive performance.
for accurate part identification and work order efficiency
for avoiding duplicates and ensuring timely sourcing
for ensuring BOM accuracy and technical specifications
for driving data consistency across ERP, EAM, and CMMS systems
for improving stocking accuracy and reducing surplus
for reducing unplanned downtime and enhancing asset performance through trusted data






Verdantis Approach to MRO Data Cleansing
Verdantis employs a sophisticated and comprehensive approach to MRO data cleansing, specifically targeting indirect materials and spare parts. Our methodology integrates cutting-edge tools with established best practices to ensure data integrity and operational efficiency. The core pillars of our process include:
Understanding the current state of your MRO data to identify areas that require cleansing and improvement.
Verifying the accuracy and completeness of your MRO data through rigorous validation processes.
Removing duplicate entries to create a clean and streamlined MRO database.
Standardizing data formats and structures to ensure consistency and compatibility across your systems.
Step-by-Step Process for MRO Data Cleansing Process from Scratch
MRO data cleansing goes beyond fixing typos or removing duplicates. It’s a structured, technical process that transforms inconsistent, legacy data into a high-quality, standardized dataset that supports maintenance, inventory, and procurement systems. Below is the step-by-step process to cleanse MRO data from scratch.
Objective: Extract raw MRO data from all relevant internal and external sources before profiling and cleansing begins.
How it works:
- Using AutoDoc AI, an intelligent document processing agent, data is automatically extracted from:
- Bill of Materials (BOMs)
- Technical manuals
- Engineering drawings
- Spreadsheets, legacy catalogs, and procurement systems
- ERP and EAM platforms (e.g., SAP, Oracle, Maximo)
- The tool parses structured and unstructured documents to isolate part descriptions, specifications, and manufacturer references.
- Data profiling tools then assess:
- Field completeness (e.g., missing part numbers or specs)
- Format inconsistencies (e.g., “KG” vs. “kg”)
- Frequency and distribution of attribute values
- Initial identification of duplicates using token and fuzzy matching algorithms
Outcome:
A consolidated, profiled, and structured MRO dataset ready for cleansing and transformation.
Objective: Group every material record under a consistent, logical mro material taxonomy for structured identification.
How it works:
- AutoTrans AI translates multilingual MRO descriptions (e.g., Arabic, Spanish, Chinese) into English for standardized classification.
- AutoClass AI agent processes translated descriptions:
- Tokenizes and semantically interprets descriptions like
“SS Hex Head Bolt 1/2-13UNC x 2.0”
→ material: Stainless Steel, form factor: Hex Head, type: Bolt, thread: 13UNC
- Tokenizes and semantically interprets descriptions like
- Items are assigned to appropriate taxonomies (e.g., UNSPSC, eCl@ss, or custom schemas)
- Uses pattern recognition and vectorization for intelligent mapping, even when input varies linguistically or structurally
Outcome:
All items are categorized accurately across languages and formats, ready for template assignment and downstream processing.
Objective: Determine the required technical attributes based on the item class.
How it works:
- Based on the classification from Step 2, each item is mapped to one of 3,700+ standardized data sheets (attribute templates).
- Each data sheet corresponds to a specific item class and contains a predefined set of attributes relevant to that class.
- These attributes define the technical, commercial, and compliance-related information necessary for the item’s usage, sourcing, and maintenance.
Example:
- Classified Item: “Centrifugal Pump, End Suction”
- Assigned Data Sheet: “Pumps – Centrifugal – End Suction – Horizontal”
- Defined Attributes:
- Flow Rate (e.g., 150 GPM)
- Head (e.g., 100 ft)
- Casing Material (e.g., Cast Iron)
- Impeller Material (e.g., Bronze)
- Suction & Discharge Size
- Power Requirement
- OEM Name & Model
Outcome:
Each item is now mapped to a relevant technical template, ensuring that it is described using a consistent, complete, and standardized set of fields.
Objective: Extract detailed specifications from unstructured text and digital artifacts.
How it works:
- AutoSpec AI, attribute extraction and data mapping agent for MRO data, analyzes item descriptions, spec sheets, drawings, and historic orders
- Attributes are parsed and assigned to fields defined in the data sheet:
- “SS Hex Bolt 1/2 x 2 in, Grade 5”
- → Material: Stainless Steel
Size: 1/2 inch x 2 inch
Grade: 5
Outcome:
Descriptions become structured and searchable data entries aligned with attribute templates.
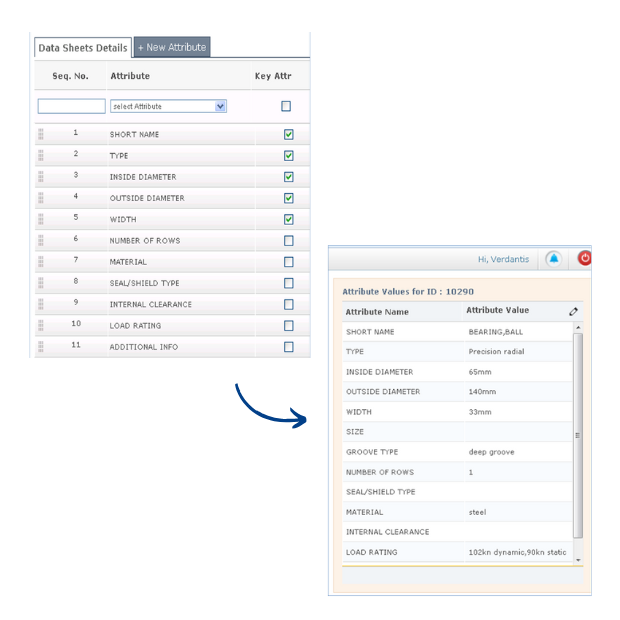
Objective: Ensure consistent representation of all values and units.
How it works:
- Abbreviation expansion: “SS” → “Stainless Steel”; “BRG” → “Bearing”
- Unit conversion: mm ↔ inch, lbs ↔ kg
- Format consistency: “RPM1800” → “1800 RPM”; “Dia 1” → “1.00 mm Diameter”
Outcome:
Data follows unified standards, eliminating variation and improving interoperability across systems.
Objective: Populate missing attributes using internal logic, reference records, and external data sources.
How it works:
- AutoEnrich AI for automated attribute extraction and mapping, cross-references:
- OEM catalogs and datasheets
- Vendor portals.
- Previously enriched internal items in the same class
- Standard templates and compliance libraries
- Enrichment can be direct (retrieved from authoritative sources) or inferred (predicted based on similar records).
Example 1: Direct Enrichment
- Original record: “Pump, Centrifugal, 5HP” with missing “Volute Material”
- AutoEnrich checks OEM catalog for the same model and finds: “Volute Material: Cast Iron”
Example 2: Contextual Inference
- 95% of internal 5HP centrifugal pump records have “Frame Type: TEFC”
- AutoEnrich suggests “TEFC” as the default value with confidence scoring
Example 3: Internet Sourcing
- AutoEnrich AI pulls in technical specs for “ABB Motor M3BP 180MLA 4” from ABB’s global catalog, filling in missing values like:
- Efficiency Class: IE3
- Insulation Class: F
- Protection Rating: IP55
Outcome:
The system fills previously missing fields with validated, credible information-resulting in complete, technically sound records that can be used confidently in maintenance, sourcing, and compliance processes.
Objective: Identify and manage outdated or inactive materials.
How it works:
- SpareSeek AI flags obsolete parts by:
- Cross-checking OEM references
- Identifying discontinued SKUs
- Tagging outdated standards or banned materials
- Suggesting modern equivalents or preferred substitutes
Example:
“GE Motor, 2HP, 208V” flagged as obsolete → Suggested replacement: “GE Motor, 2HP, 230V”
Outcome:
Obsolete items are retired or replaced, optimizing inventory and reducing risk.
Objective: Identify and consolidate duplicates at both exact-match and semantic levels.
How it works:
- L1: Token/fuzzy match (e.g., “Pump 5HP” vs. “5 HP Pump”)
- L2: Semantic clustering using NLP embeddings and attribute correlation
- Confidence scoring guides merging or manual validation
Outcome:
A de-duplicated, leaner master item list ready for accurate planning and sourcing.
Objective: Deploy the cleansed data to live systems in local language and required format.
How it works:
- English records are translated back into the original language using AutoTrans AI for deployment across multilingual environments
- Final cleansed records exported in ERP/EAM formats (SAP, Maximo, Oracle)
- Integrated workflows validate and approve records in real time via Verdantis Integrity
Outcome:
ERP-ready data is live, localized, and governed-supporting operations, compliance, and strategic planning.
Verdantis’s MRO data cleansing solution stands apart from traditional vendor offerings due to its advanced, AI-driven capabilities:
Feature | Verdantis | Traditional Vendors |
AI-powered MRO data classification via AutoEnrichAI | Yes (proprietary engine) | Limited |
Support for global taxonomies (UNSPSC, eCl@ss, NIGP) | Comprehensive | Limited |
Multi-lingual cleansing (Arabic, Spanish, Chinese & more) | Supported | English-centric |
Real-time governance workflows | Yes | Batch-based |
Seamless API integrations with ERP/EAM (SAP, Maximo, Oracle) | Provided | Limited/Manual |
Automated workflows from MRO data enrichment companies logic | Yes | Manual/Spreadsheet-based |
Governance-ready MRO data management software | Comprehensive, integrated throughout the process | Often siloed or reactive |
Business Consequences of Bad Quality Data
Managing MRO data is complex and can significantly impact operational efficiency and profitability in asset-intensive industries.
Excess Inventory & High Costs: Inaccurate data leads to overstocking, hidden inventory, and rising obsolescence and carrying costs.
Downtime & Productivity Loss: Missing or wrong data delays repairs and increases machine downtime.
Inefficient Procurement: Fragmented data weakens sourcing, inflates costs, and hinders policy compliance.
Uncontrolled Spend: Without data clarity, organizations can’t track usage, optimize spend, or negotiate better supplier terms.

EY’s client case study noted that by cleansing MRO master data, an energy company expects to save ~10% of annual MRO spend over three years via cost avoidance and inventory improvements
MRO assets are critical to production and maintenance in equipment-intensive industries. While maintenance systems like CMMS/EAM automate processes and support planning, their success depends on clean, accurate data.
Unfortunately, poor MRO data often unclassified, outdated, or incorrect, undermines these systems. It starts at data creation and spreads across the enterprise, impacting MRO inventory management, preventive maintenance, compliance, and more. The result: equipment downtime, inefficiencies, and lost revenue.
A typical “line-down” scenario shows how bad data can trigger costly disruptions.
-
Preventive Maintenance Fails:
The scenario often begins with a lack of effective preventive maintenance. Maintenance systems hold vital data (e.g., replacement frequency, equipment lifetime, inspection records). However, without a robust framework for creating this material data, it remains inconsistent and inaccurate.
This leads to a machine operating beyond its lifespan, an internal part unexpectedly breaking, and the entire production line shutting down. The immediate impact is lost production and wasted time as engineers diagnose the issue.
-
Part Search Fails:
Once the engineer identifies the needed part from OEM documentation, searching for it in the maintenance system becomes difficult due to inaccurate MRO item descriptions, cryptic entries, and a lack of vital attribute information. Even if a seemingly correct part is found, incomplete data leads to uncertainty.
This can result in requisitions for the wrong part (e.g., correct part, wrong size), further delays, and the need for rush orders when the correct part cannot be quickly located in inventory, even if it exists nearby.
-
Procurement/Spend Management Fails:
A rush order is placed with procurement. The buyer faces the same search difficulties, leading to repeated physical searches. Under extreme pressure, the buyer goes directly to the OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) for the part, bypassing lower-cost alternatives, preferred distributors, and competitive bidding.
This results in purchasing at a high markup, as the OEM may simply source and resell the component, and eliminates any chance of price negotiation or discounts.
-
Transaction Processing Fails:
Since the OEM might not be an approved supplier, the transaction must be executed manually, leading to fragmented spend data. A new, often incomplete, supplier master record must be hastily set up.
This can cause delays in invoice payments, missed early-payment discounts, and incurred interest charges. Additionally, premium rates are paid for expedited freight to minimize downtime, and sales teams must adjust delivery dates for affected orders, impacting customer commitments.
-
Inventory Fails:
Under the pressure of the breakdown, extra parts for similar machines are often ordered unnecessarily, incurring greater procurement and freight costs, plus expenses for receiving and processing unneeded inventory. Crucially, because the new item master is created under rush conditions, it may again be inaccurate.
This perpetuates the cycle, making the MRO items susceptible to being missed in inventory years later when another similar machine breaks down, potentially in a different plant.
This line-down scenario vividly demonstrates how poor MRO data generates significant unwanted costs, operational risks, and time-wasting behaviors throughout the entire production lifecycle, leaving ample scope for similar failures in the future. Accurate, clean, enriched, and classified MRO item data, harmonized to standard taxonomies, is essential to understand and manage MRO consumption patterns effectively, forming the foundation for true demand management. These challenges underscore the critical need for Master Data Management solutions.
The Business Impact of Reliable MRO Data
Implementing an AI-powered MRO data cleansing solution transforms maintenance operations, procurement, inventory management, and working capital outcomes. Here’s what leading organizations are achieving:
- 10–25% reduction in excess and obsolete inventory
- $5M–$50M+ freed from tied-up working capital (depending on scale)
- Improved parts visibility reduces duplicate orders and emergency purchases
Efficiency
- 20–30% faster work order execution due to accurate and searchable spare part data
- Reduced unplanned downtime through faster identification of critical spares
- Enhanced Preventive Maintenance (PM) through part-equipment linkage
Savings
- 15–20% reduction in MRO item procurement costs through:
- Elimination of duplicates
- Vendor consolidation
- Strategic sourcing based on clean spend data
- Shorter procurement cycles via enriched specs and manufacturer data

- Access to clean, classified, and enriched MRO data for better analytics
- Standardized MRO data taxonomy
(e.g., UNSPSC, eCl@ss) enables accurate spend, inventory, and usage reporting - Better forecasting and planning across plants and business units
- Clean data enables better performance of ERP, EAM (like Maximo or SAP PM), and CMMS systems
- Supports digital transformation goals like S/4HANA upgrades or Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
- Seamless integration of item masters across business functions
- Automated workflows ensure controlled creation and modification of MRO master data
- Centralized ownership with built-in validation rules = data quality at source
- Compliance with corporate material naming conventions and metadata policies
- Minimized equipment failure due to incorrect parts
- Avoided safety incidents from using outdated or incompatible items
- Better traceability and auditability for regulatory requirements
- Up to 40% reduction in time spent searching for parts
- Clear and standardized descriptions reduce confusion across stores, maintenance, and procurement
- Employees focus on value-added tasks rather than firefighting
- AI/ML-based platforms like Verdantis Harmonize continuously improve and scale
- Enables data governance at enterprise scale across geographies and languages
- Supports digital twins, smart asset management, and IoT-based systems

Key Benefits of MRO Data Cleansing
Enhanced Accuracy: Detects and corrects errors (e.g., conflicting part numbers), enabling confident decision-making.
Optimized Inventory: Eliminates duplicates and obsolete items, reducing excess and ensuring critical stock availability.
Improved Asset Lifecycle Management: Reliable part and maintenance data enhances asset planning and predictive maintenance.
Supply Chain Optimization: Cleansed data streamlines procurement-to-consumption processes.
Reduced Spend & Better Sourcing: Consolidated views support supplier negotiations and demand planning.
Stronger Compliance: Standardized data and workflows improve policy adherence.
Enterprise-Wide Visibility: A single source of truth reduces risk and supports governance.
Informed Strategy: Quality MRO data enables advanced analytics, better maintenance planning, and strategic growth.
Common Use Cases and Client Successes with Verdantis MRO Data Cleansing
Verdantis MRO data cleansing enterprise software’s enable clients across various asset-intensive industries to achieve significant operational improvements.
- Optimized Inventory Management: Eliminates duplicate/obsolete parts, reduces inventory bloat and carrying costs, ensuring optimal stock levels.
- Enhanced Maintenance Planning & Asset Reliability: Standardizes MRO data for accurate work orders and BOMs, leading to effective preventive maintenance and reduced downtime.
- Improved Procurement Efficiency & Cost Reduction: Enables better vendor rationalization and visibility, preventing redundant purchases and securing cost savings.
- Successful ERP/EAM Implementations & Digital Transformation: Provides clean MRO master data for smoother system migrations, better adoption, and reliable analytics.
- Robust Data Governance & Compliance: Establishes clear data standards, real-time workflows, and audit trails for ongoing data quality and reduced compliance risks.
- Streamlined Operations across Functions: Creates a single source of truth for MRO data, improving cross-functional collaboration and efficiency.
Verdantis’ enterprise software suite helps global organizations cleanse, enrich, and govern their MRO and indirect material data at scale. Deployed across complex ERP and EAM ecosystems, Verdantis AutoEnrich AI, AutoClass AI, AutoTrans AI, and Integrity enable measurable value across multiple industries.
Organizations report a 50% reduction in unplanned downtime associated with parts, a 40% reduction in inventory costs, a 35%decrease in maintenance budgets, and a 25% increase in service levels after optimizing MRO spare parts.
MRO Material Master Data Cleansing and Classification: The Next Step
Modern enterprises must do more than simply “clean” data. In asset-intensive industries, MRO master data standardization must evolve into a continuously enriched, governed, and actionable asset that integrates with maintenance systems, procurement workflows, and engineering hierarchies. Verdantis delivers this through a platform powered by agentic AI, multilingual intelligence, and deep domain logic.
Objective: Transform raw, incomplete, or inconsistent MRO descriptions into fully enriched, attribute-complete records-at scale.
Verdantis’ AutoEnrich AI and AutoSpec AI are built on natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and entity extraction engines trained on millions of industry-specific records. These agents don’t just perform a one-time MRO data enrichment-they continuously learn and evolve with each dataset iteration.
Key Capabilities:
- Attribute inference: Suggests likely attribute values based on class-level patterns (e.g., horsepower for motors, flange size for valves).
- Contextual extraction: Parses structured and semi-structured content (spec sheets, PDF catalogs, BOMs) to extract critical specs like voltage, threading, material composition, and OEM part numbers.
- Cross-verification: Matches inferred attributes with trusted external sources (OEM catalogs, vendor databases, industry data sheets) for validation.
- Feedback-driven learning: Approved enrichment decisions are used to re-train models, improving accuracy over time.
Benefits:
- Minimal human effort for large-scale enrichment
- Ability to scale across diverse product categories (electrical, mechanical, instrumentation, etc.)
- Continually improving accuracy through reinforcement learning
- Ensures compliance with global taxonomies like UNSPSC and eCl@ss
Objective: Enable global material governance and master data harmonization across regions, languages, and subsidiaries.
Verdantis’ AutoTrans AI is a language model tuned for MRO domain-specific translations. It bridges multilingual input formats and normalizes free-text descriptions to a standard enterprise-wide vocabulary.
Key Capabilities:
- Bidirectional translation of descriptions in Arabic, Spanish, German, Chinese, and more
- Terminology normalization to resolve inconsistencies like “Pump Centrifugal” vs. “Centrifugal Pump”
- Context-aware mapping: Identifies that “BB 6205” in Spanish (“Rodamiento de bolas”) maps to “Ball Bearing” in English
- Back-translation support: Ensures that enriched records can be translated back into the original language for localized ERP systems
Benefits:
- Unified global material catalog
- Eliminates cross-language duplicates
- Enables central governance while preserving regional usability
- Accelerates multilingual ERP rollouts and supplier harmonization
Objective: Create a fully traceable link between cleansed spare parts and their associated equipment assets.
Verdantis digitizes Bills of Materials (BOMs) and connects them to cleansed, enriched material masters using bill of materials inventory software. This ensures that maintenance engineers and planners access the right part, for the right asset, at the right time.
Key Capabilities:
- AutoDoc AI parses technical manuals, 2D drawings, and equipment schematics to extract part names, quantities, and locations.
- Equipment-link mapping: Spares are linked to equipment function codes and asset hierarchies within CMMS/EAM systems.
- Obsolescence mapping: If an item in the BOM is obsolete, it is flagged and mapped to an approved substitute.
- Usage validation: Historical usage patterns and failure data help validate BOM accuracy for critical assets.
Benefits:
- Reduces incorrect part usage during maintenance
- Increases first-time fix rates and minimizes downtime
- Establishes traceability between inventory and asset lifecycle
- Supports accurate preventive maintenance planning
Objective: Integrate master data, movement history, and business rules to create a single, intelligent view of MRO inventory.
Verdantis’ Inventory360 is a purpose-built inventory optimization platform for MRO environments. It blends master data quality with inventory analytics to deliver a closed-loop view of material availability, movement, and obsolescence.
Key Capabilities:
- Real-time inventory visibility across multiple plants, warehouses, and ERP instances
- Duplicate inventory clustering using semantic and attribute-based deduplication models
- Slow/non-moving part identification based on configurable thresholds for issue frequency, age, and stock rotation
- ABC and FSN analysis integrated with ERP reorder parameters to inform planning
- Lifecycle flags for obsolescence: Combines OEM support status + usage frequency to identify aging stock
Benefits:
- Reduces working capital tied in excess and redundant stock
- Enhances part availability during planned shutdowns or emergencies
- Enables inter-plant material sharing and demand aggregation
- Improves forecasting accuracy by integrating technical and transactional intelligence
Objective: Enforce enterprise-wide policies, taxonomies, and approval workflows to keep data clean and compliant at all times.
Verdantis’ Integrity platform is a governance engine that wraps every material master transaction-creation, change, deletion-with validation, approval, and auditability.
Key Capabilities:
- Role-based workflows: Defined approvers for each stage-engineering, maintenance, procurement
- Attribute-level validation rules: E.g., horsepower for motors must be numeric; manufacturer field cannot be blank
- Integration with ERP/EAM platforms: Governance enforcement at the point of data entry in SAP MDG, Oracle PIM, Maximo
- Audit trail and lineage: Every action is logged, time-stamped, and reportable
Benefits:
- Stops dirty data at the source
- Enables compliance with ISO, SOX, and safety regulations
- Reduces cycle time for material creation with in-built templates
- Makes governance scalable, visible, and collaborative
Objective: Translate clean, structured, and enriched MRO data into insights for cost reduction, risk mitigation, and operational strategy.
Verdantis provides role-based dashboards and self-service analytics, powered by AI models trained on historical data quality, sourcing behavior, and maintenance usage.
Key Capabilities:
- Inventory health dashboards: Show excess, obsolete, duplicate, and inactive materials
- Predictive analytics for spare part life expectancy, usage trends, and demand patterns
- Procurement reports: Category-level supplier consolidation and item-level sourcing variance
- Visual asset-part trees: Interactive BOMs linked to work orders and maintenance plans
Benefits:
- Improved strategic sourcing and supplier performance
- Faster root cause analysis of downtime and part failures
- Greater alignment between procurement, engineering, and plant operations
- Data-backed decision-making at every level
Objective: Ensure technicians and planners have immediate access to the right, validated materials when generating or executing maintenance work orders.
A common failure point in CMMS environments (e.g., Maximo, SAP PM) is the use of vague or incorrect material references in work orders-leading to mispicks, delays, and downtime. Verdantis eliminates this risk by embedding high-quality MRO master data into the work order lifecycle.
Key Capabilities:
- Work order-to-material linkage: Auto-recommends cleansed materials based on equipment type, location, and task history
- Contextual search assistance: Enables partial-description or attribute-based lookups (e.g., “SS Gate Valve 4in”) using semantic matching
- Spare availability check: Integrates with Inventory360 to validate part availability in local or alternate stockrooms
- Obsolescence alerts: Automatically flags if a requested part is deprecated and suggests approved substitutes
Benefits:
- Increases first-time fix rates
- Reduces delays caused by unavailable or incorrect parts
- Improves technician productivity and planning accuracy
- Ensures CMMS work orders reflect real-world material availability and spec accuracy
Example Use Case:
A planner generates a preventive maintenance work order for a centrifugal pump. The system auto-suggests the correct seal kit based on equipment model, location, and usage history-ensuring the technician pulls the right part on the first attempt.
Objective: Extend asset lifespan and minimize unplanned failures by integrating cleansed MRO data with asset hierarchies, maintenance logs, and condition monitoring systems.
In asset-intensive environments, poor linkage between materials and assets leads to inconsistent maintenance outcomes, unplanned downtime, and incorrect part substitutions. Verdantis bridges this gap by mapping structured MRO data to individual assets and enabling deep visibility across the full asset lifecycle.
Key Capabilities:
- Material-to-asset binding: Cleaned spare parts are associated with specific equipment IDs and functional locations, enabling part-level traceability.
- Failure history analysis: Enriched records allow reliability engineers to identify which parts are repeatedly linked to breakdowns or unplanned interventions.
- Predictive replacement planning: Verdantis models MTTR/MTBF (Mean Time To Repair / Mean Time Between Failures) using enriched usage and maintenance data to schedule part replacements more intelligently.
- Parts criticality classification: Each part is scored on impact to operations if unavailable, lead time, cost, safety implications, and dependency. This enables prioritized stocking and sourcing decisions.
- Example: A $12 seal with a 3-week lead time that halts a $5M packaging line if unavailable is flagged as “High Criticality.”
- Digital twin readiness: By linking spares, maintenance records, and asset performance data, Verdantis supports the creation of digital twins for scenario modeling, failure simulation, and reliability optimization.
Indirect Materials and Spare Parts MRO Data Scrubbing and Normalization
Indirect materials and spare parts form the operational backbone for manufacturing, utilities, oil & gas, and other process-driven industries. Yet, they are also the most neglected data domains-riddled with duplicates, inconsistent descriptions, missing specifications, and obsolete entries.
Why Indirect Materials & Spare Parts Data Need Cleansing
- Multiple Naming Variants
An identical item may appear in various forms across sites or systems-e.g., “Ball Bearing,” “BB 6205,” “BRG-Ball.”
- Impact: Inventory is fragmented, duplicate orders are placed, and planning suffers.
- Verdantis Fix: Enforces naming conventions through AI-driven classification and normalization, mapping each item to a unique, standardized description.
- Missing Specifications & OEM Details
Lack of attributes like size, voltage, or material results in part misuse, incorrect substitutions, or safety issues.
- Impact: Downtime, repair failures, and procurement delays.
- Verdantis Fix: AutoSpec AI and AutoEnrich AI extract and fill in specs from OEM catalogs, historical records, and contextual inference.
- Obsolete or Inactive Items
Legacy systems accumulate items that are no longer supported or used.
- Impact: Stocking unusable parts ties up capital and warehouse space.
- Verdantis Fix: Obsolescence identification and lifecycle tagging ensure active-only parts are retained.

Why the MRO Supply Chain Depends on Reliable Master Data
Master Data Management for supply chain represents a comprehensive strategy designed to establish a single, accurate, and authoritative source for a company’s critical information assets. For the MRO supply chain, an effective MDM initiative is technically bifurcated into two interdependent phases: historical data cleansing and ongoing data maintenance.
1. Historical Data Cleansing (Batch Processing & Remediation): This phase involves the systematic classification, normalization, enrichment, and de-duplication of existing legacy MRO data residing across all disparate systems, applications (e.g., ERP, SCM), and organizational units. The technical objective is to rectify historical data inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and redundancies to create a clean, standardized baseline. This provides enterprise-wide visibility into material and supplier bases, which is foundational for efficient MRO asset management and strategic supply base rationalization.
- Technical Example:
- Classification: Applying machine learning algorithms (e.g., text classification using TF-IDF or word embeddings) to categorize free-text descriptions like “Bolt SS 1/2X2” into a hierarchical taxonomy, such as Fasteners > Bolts > Hex Head Bolts, then assigning a standard code like UNSPSC 31161700.
- Technical Example:
- Normalization: Standardizing units of measure (e.g., converting “in” to “Inch” or “Lb” to “Pound”), formatting dates (MM/DD/YYYY), and expanding abbreviations (SS to Stainless Steel) using rule-based engines and lookup tables.
- De-duplication: Employing fuzzy matching algorithms (e.g., Levenshtein distance, phonetic algorithms like Soundex, or Jaro-Winkler distance) coupled with attribute comparison to identify and merge records like “PUMP, CENTRIFUGAL, 5HP” and “CENTRIFUGAL PUMP, 5 HP” into a single, canonical entry.
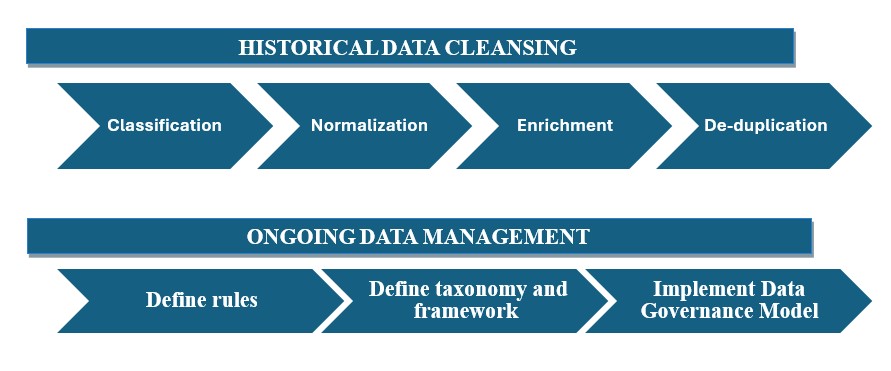
2. Ongoing Data Maintenance (ODM) (Continuous MRO Data Governance & Workflow Automation):
Beyond the initial cleansing, ODM focuses on continuously maintaining data quality by establishing a robust framework for data creation, usage, access, and maintenance across the organization. ODM ensures sustained data accuracy, enhanced operational efficiencies, and improved sourcing strategies by preventing the re-introduction of “dirty” data. It technically involves defining data collection rules, designing a structured mro material taxonomy, and implementing a comprehensive Data Governance Model (DGM).
- Technical Example:
- Data Collection Rules: Implementing data validation rules at the point of entry in ERP/MDM systems (e.g., mandatory fields for material type, minimum character length for description, allowed values from a picklist for units of measure) using configurable forms and APIs.
- Taxonomy Crafting: Designing and enforcing a multi-level, industry-standard (e.g., eCl@ss) or custom taxonomy for new MRO item creation, ensuring consistency from the outset. This often involves defining mandatory attributes for each node in the hierarchy.
3. Data Governance Model (DGM): Implementing role-based access controls (RBAC) and automated workflow engines (e.g., BPMN-based workflows) where new MRO item requests route through defined approval stages (e.g., requester, technical approver, procurement approver) with data quality checks at each step. This ensures human oversight and system-driven validation.
CMMS Optimization: The Imperative for Accurate MRO Data
CMMS platforms such as IBM Maximo, SAP PM, and Infor EAM are critical to maintenance strategy. Yet their effectiveness hinges on one factor-clean MRO data.
Without clean data:
- BOMs mismatch actual parts
- Incorrect materials are ordered
- Work orders fail due to incomplete specs
- Line stoppages and reactive maintenance surge
Example:
If a “Pump Seal” is entered without proper material (“Viton” vs “EPDM”) or dimensions, a technician might order the wrong seal → failed install → line shutdown → emergency sourcing → added cost and downtime.
Verdantis resolves this by:
- Cleaning BOM-associated parts
- Matching items to functional equipment locations
- Enabling real-time lookup and accuracy in work orders
- Enhancing planning via enriched CMMS-connected master data
Conclusion
MRO data cleansing is not merely a one-time remediation task; it represents a continuous, AI-enabled process that fundamentally underpins business agility and operational resilience. By leveraging intelligent, governance-ready solutions like those offered by Verdantis, organizations can effectively reclaim comprehensive control over their indirect material data. This foundational data integrity then empowers them to drive smarter, more informed decisions across all operational levels, from the ground up, ensuring sustained efficiency and strategic advantage.
Our commitment to robust MRO data cleansing is driven by the need to:
Adhere to industry regulations and standards by implementing MRO Data governance solutions that safeguard your MRO data.
Implementing stringent security measures to protect all MRO data, including indirect materials and spare parts, ensuring confidentiality and integrity.
Establishing clear data ownership, accountability, and stewardship for the entire MRO ecosystem to empower teams with trustworthy information for effective decision-making.
What People Ask
What does Verdantis offer for MRO data cleansing?
Verdantis provides AI-powered software solutions purpose-built for MRO data cleansing and enrichment. Our tools automate classification, deduplication, standardization, and attribute enrichment of material master data, at scale, helping enterprises build clean, consistent, and structured MRO datasets across plants and systems.
How is Verdantis different from other MRO data cleansing companies?
Unlike manual or consulting-heavy approaches, Verdantis offers configurable, automation-first software backed by deep domain taxonomies (like UNSPSC and industry-specific standards).
What sets us apart:
-
End-to-end data cleansing and enrichment with AI agents
-
Seamless ERP/EAM integration (SAP, Maximo, Oracle)
-
Multilingual support for global operations
-
Built-in governance and self-service request portals
How do data cleansing and standardization services support digital transformation?
Clean data is foundational for ERP upgrades (e.g., SAP S/4HANA), predictive maintenance, AI/ML deployment, and spend analytics. MRO data cleansing and standardization services ensure that your digital initiatives aren’t held back by inconsistent or legacy material records.
What business outcomes can we expect from MRO data cleansing and enrichment?
Typical outcomes include:
-
Inventory cost savings (10–30%) through reduced duplication and excess stock
-
Improved maintenance response times due to clearer part identification
-
Better sourcing leverage by consolidating similar SKUs
-
Higher ERP/EAM ROI through clean, classified data powering analytics and automation
These benefits directly impact your bottom line and operations.
How often should companies perform MRO data cleansing?
Best practice suggests a combination of one-time master cleansing followed by ongoing governance. Many MRO data enrichment companies offer real-time validation tools and workflows to maintain clean data continuously, avoiding the need for costly periodic cleanup.
How does MRO material master data cleansing and classification reduce inventory costs?
By eliminating duplicate and obsolete entries, and classifying materials correctly, organizations can consolidate suppliers, optimize reorder points, and reduce carrying costs. MRO material master data cleansing and classification has been shown to cut inventory value by up to 30%.
Can Verdantis handle multilingual MRO data for global companies?
Yes. Verdantis supports multi-language cleansing and enrichment, enabling global organizations to harmonize data across regional catalogs in English, Spanish, Arabic, Portuguese, Chinese, and more.
Does Verdantis support MRO data cleansing during ERP or EAM migration?
Yes. Verdantis is often deployed during large-scale digital initiatives like:
-
SAP S/4HANA transformations
-
Maximo/Oracle upgrades
-
M&A-related system integrations
Our solutions ensure clean, deduplicated, and harmonized MRO data is migrated-reducing downtime and rework during go-live.





